Alcoholic liver disease
- PMID: 22489260
- PMCID: PMC3321494
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i3.81
Alcoholic liver disease
Abstract
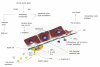
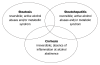
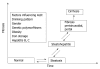
Alcohol use disorders affect millions of individuals worldwide. Alcohol consumption is directly associated with liver disease mortality and accounts for elevated social and economic costs. Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) may take the form of acute involvement (alcoholic hepatitis) or chronic liver disease (steatosis, steatohepatitis, fibrosis and cirrhosis). The severity and prognosis of alcohol-induced liver disease depends on the amount, pattern and duration of alcohol consumption, as well as on the presence of liver inflammation, diet, nutritional status and genetic predisposition of an individual. While steatosis is an almost completely benign disease, liver cirrhosis is associated with marked morbidity, mortality and life expectancy shortening. The median survival of patients with advanced cirrhosis is 1-2 years. Severe acute alcoholic hepatitis (AH) is associated with mortality as high as 50%. It has been managed with corticoids, pentoxifylline and enteral nutrition, although evidence based data are still conflicting. Some author suggest that pentoxifylline could be a better first-line treatment in patients with severe AH. Absolute abstinence is a basic condition for any treatment of acute or chronic ALD, the other therapeutical procedure being of a supportive nature and questionable significance. Acamprosate appears to be an effective treatment strategy for supporting continuous abstinence in alcohol dependent patients. Patients with advanced liver cirrhosis who demonstrably abstain can be considered for liver transplantation, which leads to a markedly prolonged life expectancy. The crucial step in ALD prevention is in the prevention of alcohol abuse, whereas the prevention of liver injury in active alcohol abusers is not clinically applicable.
Keywords: Alcohol; Alcoholic liver disease; Liver cirrhosis; Liver fibrosis; Steatohepatitis; Steatosis.
Figures
References
-
- Sherlock S, Dooley J. Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System. 11th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing; 2002. pp. 381–398.
-
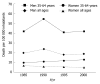
- Bosetti C, Levi F, Lucchini F, Zatonski WA, Negri E, La Vecchia C. Worldwide mortality from cirrhosis: an update to 2002. J Hepatol. 2007;46:827–839. - PubMed
-
- Caballeria J. Epidemiological aspects of alcoholic liver disease. In: Rodes J, Benhamou JP, Blei A, Reichen J, Mario Rizzetto, et al., editors. Textbook of Hepatology. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing; 2007. pp. 1129–1134.
-
- Sharma HK, Tripathi BM, Pelto PJ. The evolution of alcohol use in India. AIDS Behav. 2010;14 Suppl 1:S8–17. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

