Cumulative impact of common genetic variants and other risk factors on colorectal cancer risk in 42,103 individuals
- PMID: 22490517
- PMCID: PMC5105590
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300537
Cumulative impact of common genetic variants and other risk factors on colorectal cancer risk in 42,103 individuals
Abstract
Objective: Colorectal cancer (CRC) has a substantial heritable component. Common genetic variation has been shown to contribute to CRC risk. A study was conducted in a large multi-population study to assess the feasibility of CRC risk prediction using common genetic variant data combined with other risk factors. A risk prediction model was built and applied to the Scottish population using available data.
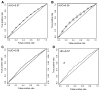
Design: Nine populations of European descent were studied to develop and validate CRC risk prediction models. Binary logistic regression was used to assess the combined effect of age, gender, family history (FH) and genotypes at 10 susceptibility loci that individually only modestly influence CRC risk. Risk models were generated from case-control data incorporating genotypes alone (n=39,266) and in combination with gender, age and FH (n=11,324). Model discriminatory performance was assessed using 10-fold internal cross-validation and externally using 4187 independent samples. The 10-year absolute risk was estimated by modelling genotype and FH with age- and gender-specific population risks.
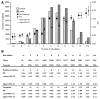
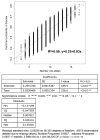
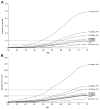
Results: The median number of risk alleles was greater in cases than controls (10 vs 9, p<2.2 × 10(-16)), confirmed in external validation sets (Sweden p=1.2 × 10(-6), Finland p=2 × 10(-5)). The mean per-allele increase in risk was 9% (OR 1.09; 95% CI 1.05 to 1.13). Discriminative performance was poor across the risk spectrum (area under curve for genotypes alone 0.57; area under curve for genotype/age/gender/FH 0.59). However, modelling genotype data, FH, age and gender with Scottish population data shows the practicalities of identifying a subgroup with >5% predicted 10-year absolute risk.
Conclusion: Genotype data provide additional information that complements age, gender and FH as risk factors, but individualised genetic risk prediction is not currently feasible. Nonetheless, the modelling exercise suggests public health potential since it is possible to stratify the population into CRC risk categories, thereby informing targeted prevention and surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest with respect to the work presented in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(2):74–108. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Parkin DM, Steliarova-Foucher E. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur J Cancer. 46(4):765–81. - PubMed
-
- Atkin WS, Edwards R, Kralj-Hans I, et al. Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 375(9726):1624–33. - PubMed
-
- Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, O’Brien MJ, et al. Randomized comparison of surveillance intervals after colonoscopic removal of newly diagnosed adenomatous polyps. The National Polyp Study Workgroup. N Engl J Med. 1993;328(13):901–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- G0000657-53203/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K/OPR/2/2/D333/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- RFA CA-95-011/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 12076/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 16459/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/94/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- C348/A12076/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA122839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127527198/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01CA122839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA143237/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K018647/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 13154/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA076783/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
