Sexual dysfunction in women with ESRD requiring hemodialysis
- PMID: 22490876
- PMCID: PMC3362315
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.12601211
Sexual dysfunction in women with ESRD requiring hemodialysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: The few existing studies of sexual dysfunction in women on hemodialysis are limited by small sample size. This large, cross-sectional study evaluated the prevalence and correlates of female sexual dysfunction in advanced kidney disease. DESIGN, SETTING, PARTICIPANTS, METHODS: A total of 1472 women with ESRD undergoing hemodialysis were recruited to a multinational, cross-sectional study conducted within a collaborative dialysis network in Europe and South America. Sexual dysfunction was identified by the Female Sexual Function Index. Correlates of self-reported sexual dysfunction were identified by regression analyses.
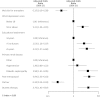
Results: Of the 1472 women, 659 completed questionnaires (45%). More than half (362 of 659 [55%]) lived with a partner, and 232 of 659 (35%) reported being sexually active. Of these 659 respondents, 555 (84%) reported sexual dysfunction. Women with a partner (282 of 362 [78%]) were less likely to report sexual dysfunction than those without a partner (273 of 297 [92%]) (P<0.001). Sexual dysfunction was independently associated with age, depressive symptoms, less education, menopause, diabetes, and diuretic therapy. Nearly all women who were not wait-listed for a kidney transplant and were living without a partner (249 of 260 [96%]) reported sexual dysfunction. More than half (128 of 232 [55%]) of sexually active women reported sexual dysfunction, associated with age, depressive symptoms, menopause, low serum albumin, and diuretic therapy.
Conclusions: This descriptive study suggests most women on hemodialysis experience sexual problems. Additional research on the relevance of sexual dysfunction to symptom burden and quality of life in these women is needed.
Figures


Comment in
-
Female sexual dysfunction in ESRD: an underappreciated epidemic?Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Jun;7(6):881-3. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03870412. Epub 2012 May 10. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22580787 No abstract available.
References
-
- Evans RW, Manninen DL, Garrison LP, Jr, Hart LG, Blagg CR, Gutman RA, Hull AR, Lowrie EG: The quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease. N Engl J Med 312: 553–559, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Bremer BA, McCauley CR, Wrona RM, Johnson JP: Quality of life in end-stage renal disease: A reexamination. Am J Kidney Dis 13: 200–209, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Merkus MP, Jager KJ, Dekker FW, Boeschoten EW, Stevens P, Krediet RT, The Necosad Study Group : Quality of life in patients on chronic dialysis: Self-assessment 3 months after the start of treatment. Am J Kidney Dis 29: 584–592, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Davison SN, Jhangri GS: Impact of pain and symptom burden on the health-related quality of life of hemodialysis patients. J Pain Symptom Manage 39: 477–485, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Stepanski E, Faber M, Zorick F, Basner R, Roth T: Sleep disorders in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 6: 192–197, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

