Tamoxifen alters the plasma concentration of molecules associated with cardiovascular risk in women with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy
- PMID: 22491005
- PMCID: PMC3336829
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0369
Tamoxifen alters the plasma concentration of molecules associated with cardiovascular risk in women with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of tamoxifen on blood markers that are associated with cardiovascular risk, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), apolipoprotein A-1 (Apo-A), and apolipoprotein B-100 (Apo-B), in women undergoing chemotherapy for breast cancer.
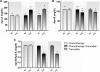
Methods: Over a period of 12 months, we followed 60 women with breast cancer. The women were divided into the following groups: a group that received only chemotherapy (n = 23), a group that received chemotherapy plus tamoxifen (n = 21), and a group that received only tamoxifen (n = 16). Plasma CRP levels were assessed at 0, 3, 6, and 12 months, and Apo-A and Apo B levels as well as the Apo-B/Apo-A ratio were assessed at 0 and 12 months.
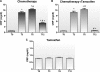
Results: We found increases in the plasma concentration of CRP in the chemotherapy alone and chemotherapy plus tamoxifen groups after 3 and 6 months of treatment (before the introduction of tamoxifen). However, after 12 months of treatment, women who used tamoxifen (the chemotherapy plus tamoxifen and tamoxifen alone groups) showed a significant reduction in CRP and Apo-B levels and a decrease in the Apo-B/Apo-A ratio. A significant increase in serum Apo-A levels was observed in the group receiving chemotherapy alone as a treatment for breast cancer.
Conclusion: The use of tamoxifen after chemotherapy for the treatment of breast cancer significantly reduces the levels of cardiovascular disease risk markers (CRP, Apo-B, and the Apo-B/Apo-A ratio).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Koukourakis MI, Kambouromiti G, Pitsiava D, et al. Serum C-reactive protein (CPR) levels in cancer patients are linked with tumor burden and are reduced by anti-hypertensive medication. Inflammation. 2009;32:169–175. - PubMed
-
- Ulrich CM, Bigler J, Potter JD. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for cancer prevention: Promise, perils, and pharmacogenetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:130–140. - PubMed
-
- Hooning MJ, Botma A, Aleman BM, et al. Long-term risk of cardiovascular disease in 10-year survivors of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:365–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

