Role for TBC1D20 and Rab1 in hepatitis C virus replication via interaction with lipid droplet-bound nonstructural protein 5A
- PMID: 22491470
- PMCID: PMC3393552
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00496-12
Role for TBC1D20 and Rab1 in hepatitis C virus replication via interaction with lipid droplet-bound nonstructural protein 5A
Abstract
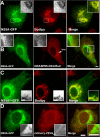
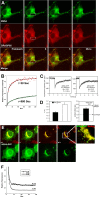
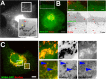
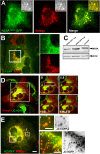
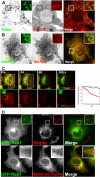
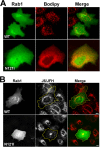
Replication and assembly of hepatitis C virus (HCV) depend on the host's secretory and lipid-biosynthetic machinery. Viral replication occurs on endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-derived modified membranes, while viral assembly is thought to occur on lipid droplets (LDs). A physical association and coordination between the viral replication and assembly complexes are prerequisites for efficient viral production. Nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A), which localizes both to the ER and LDs, is an ideal candidate for this function. Here, the interaction of NS5A with host cell membranes and binding partners was characterized in living cells. The binding of NS5A to LDs is apparently irreversible, both in HCV-infected cells and when ectopically expressed. In HCV-infected cells, NS5A fluorescence was observed around the LDs and in perinuclear structures that were incorporated into a highly immobile platform superimposed over the ER membrane. Moreover, TBC1D20 and its cognate GTPase Rab1 are recruited by NS5A to LDs. The NS5A-TBC1D20 interaction was shown to be essential for the viral life cycle. In cells, expression of the Rab1 dominant negative (Rab1DN) GTPase mutant abolished steady-state LDs. In infected cells, Rab1DN induced the elimination of NS5A from viral replication sites. Our results demonstrate the significance of the localization of NS5A to LDs and support a model whereby its interaction with TBC1D20 and Rab1 affects lipid droplet metabolism to promote the viral life cycle.
Figures
References
-
- Bartenschlager R, Penin F, Lohmann V, Andre P. 2011. Assembly of infectious hepatitis C virus particles. Trends Microbiol. 19:95–103 - PubMed
-
- Bartz R, et al. 2007. Dynamic activity of lipid droplets: protein phosphorylation and GTP-mediated protein translocation. J. Proteome Res. 6:3256–3265 - PubMed
-
- Boulant S, Targett-Adams P, McLauchlan J. 2007. Disrupting the association of hepatitis C virus core protein with lipid droplets correlates with a loss in production of infectious virus. J. Gen. Virol. 88:2204–2213 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

