Bidirectional regulation between WDR83 and its natural antisense transcript DHPS in gastric cancer
- PMID: 22491477
- PMCID: PMC3434345
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2012.57
Bidirectional regulation between WDR83 and its natural antisense transcript DHPS in gastric cancer
Abstract
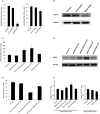
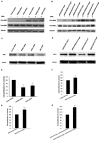
Natural antisense transcripts (NATs) exist ubiquitously in mammalian genomes and play roles in the regulation of gene expression. However, both the existence of bidirectional antisense RNA regulation and the possibility of protein-coding genes that function as antisense RNAs remain speculative. Here, we found that the protein-coding gene, deoxyhypusine synthase (DHPS), as the NAT of WDR83, concordantly regulated the expression of WDR83 mRNA and protein. Conversely, WDR83 also regulated DHPS by antisense pairing in a concordant manner. WDR83 and DHPS were capable of forming an RNA duplex at overlapping 3' untranslated regions and this duplex increased their mutual stability, which was required for the bidirectional regulation. As a pair of protein-coding cis-sense/antisense transcripts, WDR83 and DHPS were upregulated simultaneously and correlated positively in gastric cancer (GC), driving GC pathophysiology by promoting cell proliferation. Furthermore, the positive relationship between WDR83 and DHPS was also observed in other cancers. The bidirectional regulatory relationship between WDR83 and DHPS not only enriches our understanding of antisense regulation, but also provides a more complete understanding of their functions in tumor development.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

