Efficacy of OH-CATH30 and its analogs against drug-resistant bacteria in vitro and in mouse models
- PMID: 22491685
- PMCID: PMC3370729
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.06304-11
Efficacy of OH-CATH30 and its analogs against drug-resistant bacteria in vitro and in mouse models
Abstract
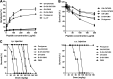
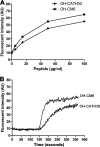
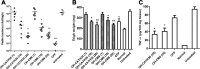
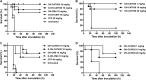
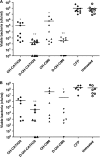
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have been considered alternatives to conventional antibiotics for drug-resistant bacterial infections. However, their comparatively high toxicity toward eukaryotic cells and poor efficacy in vivo hamper their clinical application. OH-CATH30, a novel cathelicidin peptide deduced from the king cobra, possesses potent antibacterial activity in vitro. The objective of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of OH-CATH30 and its analog OH-CM6 against drug-resistant bacteria in vitro and in vivo. The MICs of OH-CATH30 and OH-CM6 ranged from 1.56 to 12.5 μg/ml against drug-resistant clinical isolates of several pathogenic species, including Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. The MICs of OH-CATH30 and OH-CM6 were slightly altered in the presence of 25% human serum. OH-CATH30 and OH-CM6 killed E. coli quickly (within 60 min) by disrupting the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Importantly, the 50% lethal doses (LD(50)) of OH-CATH30 and OH-CM6 in mice following intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection were 120 mg/kg of body weight and 100 mg/kg, respectively, and no death was observed at any dose up to 160 mg/kg following subcutaneous (s.c.) injection. Moreover, 10 mg/kg OH-CATH30 or OH-CM6 significantly decreased the bacterial counts as well as the inflammatory response in a mouse thigh infection model and rescued infected mice in a bacteremia model induced by drug-resistant E. coli. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that the natural cathelicidin peptide OH-CATH30 and its analogs exhibit relatively low toxicity and potent efficacy in mouse models, indicating that they may have therapeutic potential against the systemic infections caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmad I, Perkins WR, Lupan DM, Selsted ME, Janoff AS. 1995. Liposomal entrapment of the neutrophil-derived peptide indolicidin endows it with in vivo antifungal activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1237:109–114 - PubMed
-
- Bommineni YR, et al. 2007. Fowlicidin-3 is an alpha-helical cationic host defense peptide with potent antibacterial and lipopolysaccharide-neutralizing activities. FEBS J. 274:418–428 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

