Clinical complexity and mortality in middle-aged and older adults with diabetes
- PMID: 22492022
- PMCID: PMC3670162
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/gls095
Clinical complexity and mortality in middle-aged and older adults with diabetes
Abstract
Background: Middle-aged and older adults with diabetes are heterogeneous and may be characterized as belonging to one of three clinical groups: a relatively healthy group, a group having characteristics likely to make diabetes self-management difficult, and a group with poor health status for whom current management targets have uncertain benefit.
Methods: We analyzed waves 2004-2008 of the Health and Retirement Study and the supplemental Health and Retirement Study 2003 Diabetes Study. The sample included adults with diabetes 51 years and older (n = 3,507, representing 13.6 million in 2004). We investigated the mortality outcomes for the three clinical groups, using survival analysis and Cox proportional hazard models.
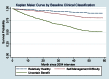
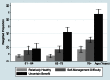
Results: The 5-year survival probabilities were Relatively Healthy Group, 90.8%; Self-Management Difficulty Group, 79.4%; and Uncertain Benefit Group, 52.5%. For all age groups and clinical groups, except those 76 years and older in the Uncertain Benefit Group, survival exceeded 50%.
Conclusions: This study reveals the substantial survival of middle-aged and older adults with diabetes, regardless of health status. These findings have implications for the clinical management of and future research about diabetes patients with multiple comorbidities.
Figures
References
-
- Selvin E, Coresh J, Brancati FL. The burden and treatment of diabetes in elderly individuals in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(11):2415–2419. - PubMed
-
- Suh DC, Kim CM, Choi IS, Plauschinat CA. Comorbid conditions and glycemic control in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, 1988 to 1994 to 1999 to 2004. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(3):484–492. - PubMed
-
- Feil DG, Zhu CW, Sultzer DL. The relationship between cognitive impairment and diabetes self-management in a population-based community sample of older adults with Type 2 diabetes. J Behav Med. 2012;35(2):190–199. - PubMed
-
- Cigolle CT, Blaum CS, Halter JB. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease prevention in older adults. Clin Geriatr Med. 2009;25(4):607–641. vii-viii. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

