Turning gene function ON and OFF using sense and antisense photo-morpholinos in zebrafish
- PMID: 22492359
- PMCID: PMC3317972
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.072702
Turning gene function ON and OFF using sense and antisense photo-morpholinos in zebrafish
Abstract
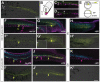
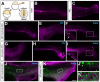
To understand the molecular mechanisms of development it is essential to be able to turn genes on and off at will and in a spatially restricted fashion. Morpholino oligonucleotides (MOs) are very common tools used in several model organisms with which it is possible to block gene expression. Recently developed photo-activated MOs allow control over the onset of MO activity. However, deactivation of photo-cleavable MO activity has remained elusive. Here, we describe photo-cleavable MOs with which it is possible to activate or de-activate MO function by UV exposure in a temporal and spatial manner. We show, using several different genes as examples, that it is possible to turn gene expression on or off both in the entire zebrafish embryo and in single cells. We use these tools to demonstrate the sufficiency of no tail expression as late as tailbud stage to drive medial precursor cells towards the notochord cell fate. As a broader approach for the use of photo-cleavable MOs, we show temporal control over gal4 function, which has many potential applications in multiple transgenic lines. We demonstrate temporal manipulation of Gal4 transgene expression in only primary motoneurons and not secondary motoneurons, heretofore impossible with conventional transgenic approaches. In another example, we follow and analyze neural crest cells that regained sox10 function after deactivation of a photo-cleavable sox10-MO at different time points. Our results suggest that sox10 function might not be critical during neural crest formation.
Figures


References
-
- Amacher S. L., Draper B. W., Summers B. R., Kimmel C. B. (2002). The zebrafish T-box genes no tail and spadetail are required for development of trunk and tail mesoderm and medial floor plate. Development 129, 3311–3323 - PubMed
-
- Appel B., Fritz A., Westerfield M., Grunwald D. J., Eisen J. S., Riley B. B. (1999). Delta-mediated specification of midline cell fates in zebrafish embryos. Curr. Biol. 9, 247–256 - PubMed
-
- Babb S. G., Barnett J., Doedens A. L., Cobb N., Liu Q., Sorkin B. C., Yelick P. C., Raymond P. A., Marrs J. A. (2001). Zebrafish E-cadherin: expression during early embryogenesis and regulation during brain development. Dev. Dyn. 221, 231–237 - PubMed
-
- Carney T. J., Dutton K. A., Greenhill E., Delfino-Machin M., Dufourcq P., Blader P., Kelsh R. N. (2006). A direct role for Sox10 in specification of neural crest-derived sensory neurons. Development 133, 4619–4630 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

