Loss of epithelial membrane protein-2 expression confers an independent prognosticator in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a cohort study
- PMID: 22492389
- PMCID: PMC3323806
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-000900
Loss of epithelial membrane protein-2 expression confers an independent prognosticator in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the expression of epithelial membrane protein-2 (EMP2) protein and its clinicopathological associations in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Design: Retrospective population-based cohort study.
Setting: This study was based on a biobank in Chi-Mei Medical Center (Tainan, Taiwan) from 1993 to 2002.
Participants: Biopsies of 124 consecutive nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients without initial distant metastasis and treated with consistent guidelines were assessed. Immunoexpressions of EMP2 were analysed and the outcomes were correlated with clinicopathological features and patient survivals.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Immunoexpressions of EMP2 were analyzed and the outcomes were correlated with clinicopathological features and patient survivals.
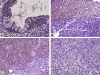
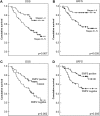
Results: Loss of EMP2 expression (49.2%) was correlated with advanced primary tumour (p=0.044), nodal status (p=0.045) and the 7th American Joint Committee on Cancer stage (p=0.027). In multivariate analyses, loss of EMP2 expression emerged as an independent prognosticator for worse disease-specific survival (DSS; p=0.015) and local recurrence-free survival (LRFS; p=0.030), along with the American Joint Committee on Cancer stages III-IV (p=0.034, DSS; p=0.023, LRFS).
Conclusions: Loss of EMP2 expression is common and associated with adverse prognosticators and might confer tumour aggressiveness through hampering its interaction with specific membrane protein(s) and hence the downstream signal transduction pathway(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chang ET, Adami HO. The enigmatic epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2006;15:1765–77 - PubMed
-
- Yu MC, Yuan JM. Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 2002;12:421–9 - PubMed
-
- Liebowitz D. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: the Epstein-Barr virus association. Semin Oncol 1994;21:376–81 - PubMed
-
- Lo KW, To KF, Huang DP. Focus on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2004;5:423–8 - PubMed
-
- Fang FM, Chien CY, Li CF, et al. Effect of S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 expression on distant metastasis and survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;73:202–7 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
