Combinatorial targeting of ribbon-helix-helix artificial transcription factors to chimeric recognition sites
- PMID: 22492712
- PMCID: PMC3413123
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks314
Combinatorial targeting of ribbon-helix-helix artificial transcription factors to chimeric recognition sites
Abstract
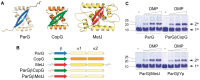
Artificial transcription factors (ATFs) are potent synthetic biology tools for modulating endogenous gene expression and precision genome editing. The ribbon-helix-helix (RHH) superfamily of transcription factors are widespread in bacteria and archaea. The principal DNA binding determinant in this family comprises a two-stranded antiparallel β-sheet (ribbons) in which a pair of eight-residue motifs insert into the major groove. Here, we demonstrate that ribbons of divergent RHH proteins are compact and portable elements that can be grafted into a common α-helical scaffold producing active ATFs. Hybrid proteins cooperatively recognize DNA sites possessing core tetramer boxes whose functional spacing is dictated by interactions between the α-helical backbones. These interactions also promote combinatorial binding of chimeras with different transplanted ribbons, but identical backbones, to synthetic sites bearing cognate boxes for each protein either in vitro or in vivo. The composite assembly of interacting hybrid proteins offers potential advantages associated with combinatorial approaches to DNA recognition compared with ATFs that involve binding of a single protein. Moreover, the new class of RHH ATFs may be utilized to re-engineer transcriptional circuits, or may be enhanced with affinity tags, fluorescent moieties or other elements for targeted genome marking and manipulation in bacteria and archaea.
Figures



References
-
- Stormo GD, Zhao Y. Determining the specificity of protein-DNA interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:751–760. - PubMed
-
- Garvie CW, Wolberger C. Recognition of specific DNA sequences. Mol. Cell. 2001;8:937–946. - PubMed
-
- Ansari AZ, Mapp AK. Modular design of artificial transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002;6:765–772. - PubMed
-
- Collins CH, Yokobayashi Y, Umeno D, Arnold FH. Engineering proteins that bind, move, make and break DNA. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003;14:371–378. - PubMed

