Requirement of the cytosolic interaction between PATHOGENESIS-RELATED PROTEIN10 and LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT PROTEIN1 for cell death and defense signaling in pepper
- PMID: 22492811
- PMCID: PMC3398571
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.112.095869
Requirement of the cytosolic interaction between PATHOGENESIS-RELATED PROTEIN10 and LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT PROTEIN1 for cell death and defense signaling in pepper
Abstract
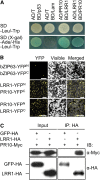
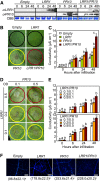
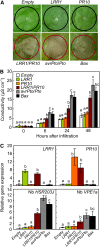
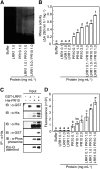
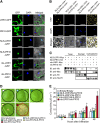
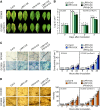
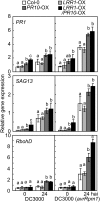
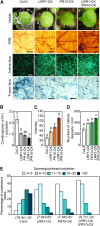
Plants recruit innate immune receptors such as leucine-rich repeat (LRR) proteins to recognize pathogen attack and activate defense genes. Here, we identified the pepper (Capsicum annuum) pathogenesis-related protein10 (PR10) as a leucine-rich repeat protein1 (LRR1)-interacting partner. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation and coimmunoprecipitation assays confirmed the specific interaction between LRR1 and PR10 in planta. Avirulent Xanthomonas campestris pv vesicatoria infection induces PR10 expression associated with the hypersensitive cell death response. Transient expression of PR10 triggers hypersensitive cell death in pepper and Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, which is amplified by LRR1 coexpression as a positive regulator. LRR1 promotes the ribonuclease activity and phosphorylation of PR10, leading to enhanced cell death signaling. The LRR1-PR10 complex is formed in the cytoplasm, resulting in its secretion into the apoplastic space. Engineered nuclear confinement of both proteins revealed that the cytoplasmic localization of the PR10-LRR1 complex is essential for cell death-mediated defense signaling. PR10/LRR1 silencing in pepper compromises resistance to avirulent X. campestris pv vesicatoria infection. By contrast, PR10/LRR1 overexpression in Arabidopsis thaliana confers enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato and Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Together, these results suggest that the cytosolic LRR-PR10 complex is responsible for cell death-mediated defense signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Barna B., Ibenthal W.D., Heitefuss R. (1989). Extracellular RNase activity in healthy and rust-infected wheat leaves. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 35: 151–160
-
- Bufe A., Spangfort M.D., Kahlert H., Schlaak M., Becker W.-M. (1996). The major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1, shows ribonuclease activity. Planta 199: 413–415 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

