Ube3a-ATS is an atypical RNA polymerase II transcript that represses the paternal expression of Ube3a
- PMID: 22493002
- PMCID: PMC3465693
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/dds130
Ube3a-ATS is an atypical RNA polymerase II transcript that represses the paternal expression of Ube3a
Abstract
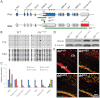
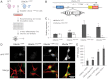
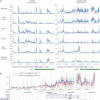
The Angelman syndrome gene, UBE3A, is subject to genomic imprinting controlled by mechanisms that are only partially understood. Its antisense transcript, UBE3A-ATS, is also imprinted and hypothesized to suppress UBE3A in cis. In this research, we showed that the mouse antisense ortholog, Ube3a-ATS, was transcribed by RNA polymerase (RNAP) II. However, unlike typical protein-coding transcripts, Ube3a-ATS was not poly-adenylated and was localized exclusively in the nucleus. It was relatively unstable with a half-life of 4 h, shorter than most protein-coding RNAs tested. To understand the role of Ube3a-ATS in vivo, a mouse model with a 0.9-kb genomic deletion over the paternal Snrpn major promoter was studied. The mice showed partial activation of paternal Ube3a, with decreased expression of Ube3a-ATS but not any imprinting defects in the Prader-Willi syndrome/Angelman syndrome region. A novel cell culture model was also generated with a transcriptional termination cassette inserted downstream of Ube3a on the paternal chromosome to reduce Ube3a-ATS transcription. In neuronally differentiated embryonic stem (ES) cells, paternal Ube3a was found to be expressed at a high level, comparable with that of the maternal allele. To further characterize the antisense RNA, a strand-specific microarray was performed. Ube3a-ATS was detectable across the entire locus of Ube3a and extended beyond the transcriptional start site of Ube3a. In summary, we conclude that Ube3a-ATS is an atypical RNAPII transcript that represses Ube3a on the paternal chromosome. These results suggest that the repression of human UBE3A-ATS may activate the expression of UBE3A from the paternal chromosome, providing a potential therapeutic strategy for patients with Angelman syndrome.
Figures

References
-
- Edwards C.A., Ferguson-Smith A.C. Mechanisms regulating imprinted genes in clusters. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007;19:281–289. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2007.04.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Horsthemke B. Mechanisms of imprint dysregulation. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2010;154C:321–328. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.30269. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buiting K. Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2010;154C:365–376. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.30273. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Horsthemke B., Wagstaff J. Mechanisms of imprinting of the Prader-Willi/Angelman region. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2008;146A:2041–2052. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32364. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kantor B., Makedonski K., Green-Finberg Y., Shemer R., Razin A. Control elements within the PWS/AS imprinting box and their function in the imprinting process. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004;13:751–762. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh085. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

