TASK-3 channel deletion in mice recapitulates low-renin essential hypertension
- PMID: 22493079
- PMCID: PMC3357084
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.189662
TASK-3 channel deletion in mice recapitulates low-renin essential hypertension
Erratum in
- Hypertension. 2012 Jun;59(6):e59
Abstract
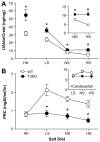
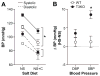
Idiopathic primary hyperaldosteronism (IHA) and low-renin essential hypertension (LREH) are common forms of hypertension, characterized by an elevated aldosterone-renin ratio and hypersensitivity to angiotensin II. They are suggested to be 2 states within a disease spectrum that progresses from LREH to IHA as the control of aldosterone production by the renin-angiotensin system is weakened. The mechanism(s) that drives this progression remains unknown. Deletion of Twik-related acid-sensitive K(+) channels (TASK) subunits, TASK-1 and TASK-3, in mice (T1T3KO) produces a model of human IHA. Here, we determine the effect of deleting only TASK-3 (T3KO) on the control of aldosterone production and blood pressure. We find that T3KO mice recapitulate key characteristics of human LREH, salt-sensitive hypertension, mild overproduction of aldosterone, decreased plasma-renin concentration with elevated aldosterone:renin ratio, hypersensitivity to endogenous and exogenous angiotensin II, and failure to suppress aldosterone production with dietary sodium loading. The relative differences in levels of aldosterone output and aldosterone:renin ratio and in autonomy of aldosterone production between T1T3KO and T3KO mice are reminiscent of differences in human hypertensive patients with LREH and IHA. Our studies establish a model of LREH and suggest that loss of TASK channel activity may be one mechanism that advances the syndrome of low renin hypertension.
Figures
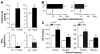


References
-
- Funder JW, Carey RM, Fardella C, Gomez-Sanchez CE, Mantero F, Stowasser M, Young WF, Jr, Montori VM. Case detection, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with primary aldosteronism: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:3266–3281. - PubMed
-
- Gordon RD, Laragh JH, Funder JW. Low renin hypertensive states: Perspectives, unsolved problems, future research. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005;16:108–113. - PubMed
-
- Mulatero P, Verhovez A, Morello F, Veglio F. Diagnosis and treatment of low-renin hypertension. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2007;67:324–334. - PubMed
-
- Stowasser M, Gordon RD. The aldosterone-renin ratio and primary aldosteronism. Mayo Clin Proc. 2002;77:202–203. - PubMed
-
- Tomaschitz A, Maerz W, Pilz S, Ritz E, Scharnagl H, Renner W, Boehm BO, Fahrleitner-Pammer A, Weihrauch G, Dobnig H. Aldosterone/renin ratio determines peripheral and central blood pressure values over a broad range. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:2171–2180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

