B-type natriuretic Peptide assay for the diagnosis and prognosis of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants
- PMID: 22493614
- PMCID: PMC3318091
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.3.192
B-type natriuretic Peptide assay for the diagnosis and prognosis of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants
Abstract
Background and objectives: Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in preterm infants. Measurement of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) has been reported to be a useful bedside screening tool for the presence of hemodynamically significant PDA (hsPDA) in neonates. This study was conducted to investigate the usefulness of a BNP assay as a biochemical marker for the diagnosis of hsPDA and predictive biomarker of the response to indomethacin in preterm infants.
Subjects and methods: Preterm infants born at <37 weeks' gestational age were prospectively enrolled within 24 hours of birth. Plasma BNP levels were measured on days 1, 4, and 7. Significant PDA was diagnosed by large ductal flow with left to right shunt on color Doppler echocardiography, along with clinical features of PDA. Following that, hsPDA was treated with indomethacin.
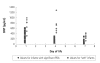
Results: A total of 28 preterm infants were prospectively enrolled in this study. Seven infants with PDA had higher on day 4 plasma BNP values (median 654.68 pg/mL; range 428.29-1280.00) compared to the control group (median 124.52 pg/mL; range 37.21-290.49). The area under the receiver operator characteristic curve for the detection of hsPDA was high: 0.998 (95% confidence interval: 0.995-1.002). The cutoff of BNP concentration for the diagnosis of hsPDA was determined to be 412 pg/mL (sensitivity: 100%; specificity: 95%).
Conclusion: B-type natriuretic peptide can be a useful biomarker for the screening and diagnosis of PDA in preterm infants. Serial BNP measurements are valuable for assessing the clinical course and indomethacin responsiveness of PDA.
Keywords: B-type natriuretic peptide; Echocardiography; Patent ductus arteriosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Utility of rapid B-type natriuretic peptide assay for diagnosis of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants.Pediatrics. 2005 Mar;115(3):e255-61. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1837. Epub 2005 Feb 1. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 15687418 Clinical Trial.
-
N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide: a measure of significant patent ductus arteriosus.Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008 Jul;93(4):F257-60. doi: 10.1136/adc.2007.120691. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008. PMID: 18218660
-
Role of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide in screening for hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in preterm neonates.J Perinatol. 2005 Nov;25(11):709-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211383. J Perinatol. 2005. PMID: 16222347
-
Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants.Indian Pediatr. 2011 Apr;48(4):301-8. doi: 10.1007/s13312-011-0062-5. Indian Pediatr. 2011. PMID: 21532100 Review.
-
Prediction of Therapeutic Response to Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors in Preterm Infants with Patent Ductus Arteriosus.Pediatr Cardiol. 2018 Apr;39(4):647-652. doi: 10.1007/s00246-018-1831-x. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Pediatr Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29468349 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Neonatal Diseases.Front Pediatr. 2021 Dec 7;9:767173. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.767173. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34950618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Individualized ibuprofen treatment using serial B-type natriuretic peptide measurement for symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in very preterm infants.Korean J Pediatr. 2017 Jun;60(6):175-180. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2017.60.6.175. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Korean J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28690644 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of B-type natriuretic peptide levels and echocardiographic parameters in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus.Korean J Pediatr. 2016 Apr;59(4):183-9. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2016.59.4.183. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Korean J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27186229 Free PMC article.
-
[B-type brain natriuretic peptide as marker of hemodynamic overload of the patent ductus arteriosus in the preterm infant].Arch Cardiol Mex. 2020 Nov 3;91(1):17-24. doi: 10.24875/ACM.19000398. Arch Cardiol Mex. 2020. PMID: 33142312 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
Brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide for the diagnosis of haemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in preterm neonates.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 8;12(12):CD013129. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013129.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36478359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bancalari E, Claure N, Gonzalez A. Patent ductus arteriosus and respiratory outcome in premature infants. Biol Neonate. 2005;88:192–201. - PubMed
-
- Clyman RI. Ductus arteriosus: current theories of prenatal and postnatal regulation. Semin Perinatol. 1987;11:64–71. - PubMed
-
- Heymann MA, Rudolf AM. Control of the ductus arteriosus. Physiol Rev. 1975;55:62–78. - PubMed
-
- Clyman RI. Mechanisms regulating the ductus arteriosus. Biol Neonate. 2006;89:330–335. - PubMed
-
- Rojas MA, Gonzalez A, Bancalari E, Claure N, Poole C, Silva-Neto G. Changing trends in the epidemiology and pathogenesis of neonatal chronic lung disease. J Pediatr. 1995;126:605–610. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

