A rapid, cost-effective method of assembly and purification of synthetic DNA probes >100 bp
- PMID: 22493688
- PMCID: PMC3321010
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034373
A rapid, cost-effective method of assembly and purification of synthetic DNA probes >100 bp
Abstract
Here we introduce a rapid, cost-effective method of generating molecular DNA probes in just under 15 minutes without the need for expensive, time-consuming gel-extraction steps. As an example, we enzymatically concatenated six variable strands (50 bp) with a common strand sequence (51 bp) in a single pool using Fast-Link DNA ligase to produce 101 bp targets (10 min). Unincorporated species were then filtered out by passing the crude reaction through a size-exclusion column (<5 min). We then compared full-length product yield of crude and purified samples using HPLC analysis; the results of which clearly show our method yields three-quarters that of the crude sample (50% higher than by gel-extraction). And while we substantially reduced the amount of unligated product with our filtration process, higher purity and yield, with an increase in number of stands per reaction (>12) could be achieved with further optimization. Moreover, for large-scale assays, we envision this method to be fully automated with the use of robotics such as the Biomek FX; here, potentially thousands of samples could be pooled, ligated and purified in either a 96, 384 or 1536-well platform in just minutes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
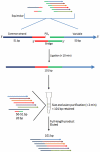
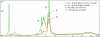
References
-
- Fredriksson S, Dixon W, Ji H, Koong AC, Mindrinos M, et al. Multiplexed protein detection by proximity ligation for cancer biomarker validation. Nat Methods. 2007;4:327–329. - PubMed
-
- Hardenbol P, Baner J, Jain M, Nilsson M, Namsaraev EA, et al. Multiplexed genotyping with sequence-tagged molecular inversion probes. Nature biotechnology. 2003;21:673–678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

