Lack of an endogenous GABAA receptor-mediated tonic current in hypoglossal motoneurons
- PMID: 22495589
- PMCID: PMC3406384
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.231944
Lack of an endogenous GABAA receptor-mediated tonic current in hypoglossal motoneurons
Abstract
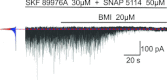
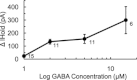
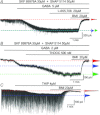
Tonic GABAA receptor-mediated current is an important modulator of neuronal excitability, but it is not known if it is present in mammalian motoneurons. To address this question studies were performed using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from mouse hypoglossal motoneurons (HMs) in an in vitro slice preparation. In the presence of blockers of glutamatergic and glycinergic receptor-mediated transmission application of SR-95531 or bicuculline, while abolishing GABAA receptor-mediated phasic synaptic currents, did not reveal a tonic GABAA receptor-mediated current. Additionally, blockade of both GAT-1 and GAT-3 GABA transporters did not unmask this tonic current. In contrast, application of exogenous GABA (1 to 15 μm) resulted in a tonic GABAergic current that was observed when both GAT-1 and GAT-3 transporters were simultaneously blocked, and this current was greater than the sum of the current observed when each transporter was blocked individually. We also investigated which GABAA receptor subunits may be responsible for the current. Application of the δ subunit GABAA receptor agonist THIP resulted in a tonic GABAA receptor current. Application of the δ subunit modulator THDOC resulted in an enhanced tonic current. Application of the α5 subunit GABAA receptor inverse agonist L-655,708 did not modulate the current. In conclusion, these data show that HMs have tonic GABAA receptor-mediated current. The level of GABA in the vicinity of GABAA receptors responsible for this current is regulated by GABA transporters. In HMs a tonic current in response to exogenous GABA probably arises from activation of GABAA receptors containing δ subunits.
Figures

References
-
- Altschuler SM, Bao X, Miselis RR. Dendritic architecture of hypoglossal motoneurons projecting to extrinsic tongue musculature in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1994;342:538–550. - PubMed
-
- Bonin RP, Martin LJ, MacDonald JF, Orser BA. α5GABAA receptors regulate the intrinsic excitability of mouse hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2007;98:2244–2254. - PubMed
-
- Borden LA. GABA transporter heterogeneity: pharmacology and cellular localization. Neurochem Int. 1996;29:335–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

