The parametric g-formula to estimate the effect of highly active antiretroviral therapy on incident AIDS or death
- PMID: 22495733
- PMCID: PMC3641816
- DOI: 10.1002/sim.5316
The parametric g-formula to estimate the effect of highly active antiretroviral therapy on incident AIDS or death
Abstract
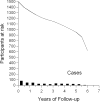
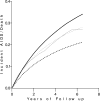
The parametric g-formula can be used to contrast the distribution of potential outcomes under arbitrary treatment regimes. Like g-estimation of structural nested models and inverse probability weighting of marginal structural models, the parametric g-formula can appropriately adjust for measured time-varying confounders that are affected by prior treatment. However, there have been few implementations of the parametric g-formula to date. Here, we apply the parametric g-formula to assess the impact of highly active antiretroviral therapy on time to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) or death in two US-based human immunodeficiency virus cohorts including 1498 participants. These participants contributed approximately 7300 person-years of follow-up (49% exposed to highly active antiretroviral therapy) during which 382 events occurred and 259 participants were censored because of dropout. Using the parametric g-formula, we estimated that antiretroviral therapy substantially reduces the hazard of AIDS or death (hazard ratio = 0.55; 95% confidence limits [CL]: 0.42, 0.71). This estimate was similar to one previously reported using a marginal structural model, 0.54 (95% CL: 0.38, 0.78). The 6.5-year difference in risk of AIDS or death was 13% (95% CL: 8%, 18%). Results were robust to assumptions about temporal ordering, and extent of history modeled, for time-varying covariates. The parametric g-formula is a viable alternative to inverse probability weighting of marginal structural models and g-estimation of structural nested models for the analysis of complex longitudinal data.
Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Robins JM. A new approach to causal inference in mortality studies with sustained exposure periods – application to control of the healthy worker survivor effect. Mathe Model. 1986;7:1393–1512.
-
- Robins JM. Structural nested failure time models. In: Armitage P, Colton T, editors. Encyclopedia of Biostatistics. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons; 1998. pp. 4372–4389.
-
- Robins JM, Hernán MA, Brumback B. Marginal structural models and causal inference in epidemiology. Epidemiology. 2000;11:550–560. - PubMed
-
- Hernán MA, Hernandez-Diaz S, Robins JM. A structural approach to selection bias. Epidemiology. 2004;15(5):615–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HD-32632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HD063961/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AA-017594/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI073127/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007001/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-42590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5-M01-RR-00052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-34994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI-50410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HD063961/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA017594/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-31834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI-073127-01A2/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 AI 07001-32/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-34993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K99-HD-063961/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-34989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
