Low dose ionizing radiation produces too few reactive oxygen species to directly affect antioxidant concentrations in cells
- PMID: 22496076
- PMCID: PMC3391473
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2012.0150
Low dose ionizing radiation produces too few reactive oxygen species to directly affect antioxidant concentrations in cells
Abstract
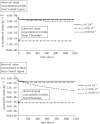
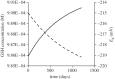
It has been hypothesized that radiation-induced oxidative stress is the mechanism for a wide range of negative impacts on biota living in radioactively contaminated areas around Chernobyl. The present study tests this hypothesis mechanistically, for the first time, by modelling the impacts of radiolysis products within the cell resulting from radiations (low linear energy transfer β and γ), and dose rates appropriate to current contamination types and densities in the Chernobyl exclusion zone and at Fukushima. At 417 µGy h(-1) (illustrative of the most contaminated areas at Chernobyl), generation of radiolysis products did not significantly impact cellular concentrations of reactive oxygen species, or cellular redox potential. This study does not support the hypothesis that direct oxidizing stress is a mechanism for damage to organisms exposed to chronic radiation at dose rates typical of contaminated environments.
Figures
References
-
- Monaghan P., Metcalfe N. B., Torres R. 2009. Oxidative stress as a mediator of life history trade-offs: mechanisms, measurements and interpretation. Ecol. Lett. 12, 75–92 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01258.x (doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01258.x) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weiss J. F., Landauer M. R. 2003. Protection against ionizing radiation by antioxidant nutrients and phytochemicals. Toxicology 189, 1–20 10.1016/S0300-483X(03)00149-5 (doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(03)00149-5) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Esnault M.-A., Legue F., Chenal C. 2010. Ionizing radiation: advances in plant response. Environ. Exp. Bot. 68, 231–237 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.01.007 (doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.01.007) - DOI
-
- Møller A. P., Surai P., Mousseau T. A. 2005. Antioxidants, radiation and mutation as revealed by sperm abnormality in barn swallows from Chernobyl. Proc. R. Soc. B 272, 247–253 10.1098/rspb.2004.2914 (doi:10.1098/rspb.2004.2914) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zaka R., Vandecasteele C. M., Misset M. T. 2002. Effects of low chronic doses of ionizing radiation on antioxidant enzymes and G6PDH activities in Stipa capillata (Poaceae). J. Exp. Bot. 53, 1979–1987 10.1093/jxb/erf041 (doi:10.1093/jxb/erf041) - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
