A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of antidepressants in Parkinson disease
- PMID: 22496199
- PMCID: PMC3324323
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182516244
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of antidepressants in Parkinson disease
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) and a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) in the treatment of depression in Parkinson disease (PD).
Methods: A total of 115 subjects with PD were enrolled at 20 sites. Subjects were randomized to receive an SSRI (paroxetine; n = 42), an SNRI (venlafaxine extended release [XR]; n = 34), or placebo (n = 39). Subjects met DSM-IV criteria for a depressive disorder, or operationally defined subsyndromal depression, and scored >12 on the first 17 items of the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D). Subjects were followed for 12 weeks (6-week dosage adjustment, 6-week maintenance). Maximum daily dosages were 40 mg for paroxetine and 225 mg for venlafaxine XR. The primary outcome measure was change in the HAM-D score from baseline to week 12.
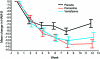
Results: Treatment effects (relative to placebo), expressed as mean 12-week reductions in HAM-D score, were 6.2 points (97.5% confidence interval [CI] 2.2 to 10.3, p = 0.0007) in the paroxetine group and 4.2 points (97.5% CI 0.1 to 8.4, p = 0.02) in the venlafaxine XR group. No treatment effects were seen on motor function.
Conclusions: Both paroxetine and venlafaxine XR significantly improved depression in subjects with PD. Both medications were generally safe and well tolerated and did not worsen motor function.
Classification of evidence: This study provides Class I evidence that paroxetine and venlafaxine XR are effective in treating depression in patients with PD.
Figures

Comment in
-
Glad about SAD (PD).Neurology. 2012 Apr 17;78(16):1198-9. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318250d88c. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Neurology. 2012. PMID: 22496197 No abstract available.
References
-
- Liu C-Y, Wang S-J, Fuh J-L, Lin C-H, Yang Y-Y, Liu H-C. The correlation of depression with functional activity in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol 1997;244:493–498 - PubMed
-
- Kuopio A, Marttila R, Hellenius H, Toivonen M, Rinne U. The quality of life in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2000;15:216–223 - PubMed
-
- Phillips P. Keeping depression at bay helps patients with Parkinson's disease. JAMA 1999;282:1118–1119 - PubMed
-
- The Global Parkinson's Disease Survey (GPDS) Steering Committee Factors impacting on quality of life in Parkinson's disease: results from an international survey. Mov Disord 2001;17:60–67 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
