Mice deficient in STAT1 but not STAT2 or IRF9 develop a lethal CD4+ T-cell-mediated disease following infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus
- PMID: 22496215
- PMCID: PMC3393544
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.07147-11
Mice deficient in STAT1 but not STAT2 or IRF9 develop a lethal CD4+ T-cell-mediated disease following infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus
Abstract
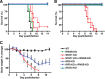
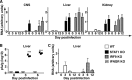
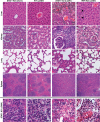
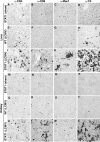
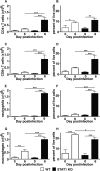
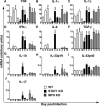
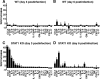
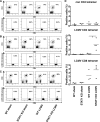
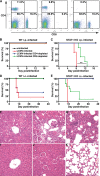
Interferon (IFN) signaling is crucial for antiviral immunity. While type I IFN signaling is mediated by STAT1, STAT2, and IRF9, type II IFN signaling requires only STAT1. Here, we studied the roles of these signaling factors in the host response to systemic infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV). In wild-type (WT) mice and mice lacking either STAT2 or IRF9, LCMV infection was nonlethal, and the virus either was cleared (WT) or established persistence (STAT2 knockout [KO] and IRF9 KO). However, in the case of STAT1 KO mice, LCMV infection was lethal and accompanied by severe multiorgan immune pathology, elevated expression of various cytokine genes in tissues, and cytokines in the serum. This lethal phenotype was unaltered by the coabsence of the gamma interferon (IFN-γ) receptor and hence was not dependent on IFN-γ. Equally, the disease was not due to a combined defect in type I and type II IFN signaling, as IRF9 KO mice lacking the IFN-γ receptor survived infection with LCMV. Clearance of LCMV is mediated normally by CD8(+) T cells. However, the depletion of these cells in LCMV-infected STAT1 KO mice was delayed, but did not prevent, lethality. In contrast, depletion of CD4(+) T cells prevented lethality in LCMV-infected STAT1 KO mice and was associated with a reduction in tissue immune pathology. These studies highlight a fundamental difference in the role of STAT1 versus STAT2 and IRF9. While all three factors are required to limit viral replication and spread, only STAT1 has the unique function of preventing the emergence of a lethal antiviral CD4(+) T-cell response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IRF7-dependent type I interferon production induces lethal immune-mediated disease in STAT1 knockout mice infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus.J Virol. 2014 Jul;88(13):7578-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03117-13. Epub 2014 Apr 23. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24760883 Free PMC article.
-
IRF9 Prevents CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion in an Extrinsic Manner during Acute Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Oct 27;91(22):e01219-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01219-17. Print 2017 Nov 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28878077 Free PMC article.
-
Type I interferon-regulated gene expression and signaling in murine mixed glial cells lacking signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 or 2 or interferon regulatory factor 9.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 7;292(14):5845-5859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.756510. Epub 2017 Feb 17. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28213522 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of interferon regulatory factor 9 in the antiviral host response and beyond.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Jun;29:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 26987614 Review.
-
The unique role of STAT2 in constitutive and IFN-induced transcription and antiviral responses.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Jun;29:71-81. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.02.010. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 27053489 Review.
Cited by
-
STAT2 and IRF9: Beyond ISGF3.JAKSTAT. 2013 Oct 1;2(4):e27521. doi: 10.4161/jkst.27521. Epub 2013 Dec 18. JAKSTAT. 2013. PMID: 24498542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT1-Deficient HPV E6/E7-Associated Cancers Maintain Host Immunocompetency against Therapeutic Intervention.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Apr 17;12(4):430. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12040430. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675812 Free PMC article.
-
Restriction of Viral Replication, Rather than T Cell Immunopathology, Drives Lethality in Murine Norovirus CR6-Infected STAT1-Deficient Mice.J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0206521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02065-21. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35107369 Free PMC article.
-
Non-redundant ISGF3 Components Promote NK Cell Survival in an Auto-regulatory Manner during Viral Infection.Cell Rep. 2018 Aug 21;24(8):1949-1957.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.060. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30134157 Free PMC article.
-
Complexities of Type I Interferon Biology: Lessons from LCMV.Viruses. 2019 Feb 20;11(2):172. doi: 10.3390/v11020172. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30791575 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aichele P, et al. 2006. CD8 T cells specific for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus require type I IFN receptor for clonal expansion. J. Immunol. 176:4525–4529 - PubMed
-
- Allan JE, Doherty PC. 1990. Binding of monoclonal antibodies and T cell effector function in vivo. Hybridoma 9:9–15 - PubMed
-
- Alsharifi M, Mullbacher A, Regner M. 2008. Interferon type I responses in primary and secondary infections. Immunol. Cell Biol. 86:239–245 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

