NHERF1 acts as a molecular switch to program metastatic behavior and organotropism via its PDZ domains
- PMID: 22496422
- PMCID: PMC3364169
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-11-0911
NHERF1 acts as a molecular switch to program metastatic behavior and organotropism via its PDZ domains
Abstract
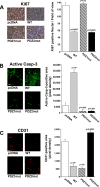
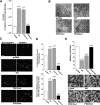
Metastatic cells are highly plastic for differential expression of tumor phenotype hallmarks and metastatic organotropism. The signaling proteins orchestrating the shift of one cell phenotype and organ pattern to another are little known. Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor (NHERF1) is a molecular pathway organizer, PDZ-domain protein that recruits membrane, cytoplasmic, and cytoskeletal signaling proteins into functional complexes. To gain insight into the role of NHERF1 in metastatic progression, we stably transfected a metastatic breast cell line, MDA-MB-231, with an empty vector, with wild-type NHERF1, or with NHERF1 mutated in either the PDZ1- or PDZ2-binding domains to block their binding activities. We observed that NHERF1 differentially regulates the expression of two phenotypic programs through its PDZ domains, and these programs form the mechanistic basis for metastatic organotropism. The PDZ2 domain promotes visceral metastases via increased invadopodia-dependent invasion and anchorage-independent growth, as well as by inhibition of apoptosis, whereas the PDZ1 domain promotes bone metastases by stimulating podosome nucleation, motility, neoangiogenesis, vasculogenic mimicry, and osteoclastogenesis in the absence of increased growth or invasion. Collectively, these findings identify NHERF1 as an important signaling nexus for coordinating cell structure with metastatic behavior and identifies the "mesenchymal-to-vasculogenic" phenotypic transition as an essential step in metastatic progression.
Figures





References
-
- Arguello F, Baggs RB, Frantz CN. A murine model of experimental metastasis to bone and bone marrow. Cancer Res. 1988;48:6876–6881. - PubMed
-
- Basbaum CB, Werb Z. Focalized proteolysis: spatial and temporal regulation of extracellular matrix degradation at the cell surface. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:731–738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

