Power-law decay of the spatial correlation function in exciton-polariton condensates
- PMID: 22496595
- PMCID: PMC3340049
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1107970109
Power-law decay of the spatial correlation function in exciton-polariton condensates
Abstract
We create a large exciton-polariton condensate and employ a Michelson interferometer setup to characterize the short- and long-distance behavior of the first order spatial correlation function. Our experimental results show distinct features of both the two-dimensional and nonequilibrium characters of the condensate. We find that the gaussian short-distance decay is followed by a power-law decay at longer distances, as expected for a two-dimensional condensate. The exponent of the power law is measured in the range 0.9-1.2, larger than is possible in equilibrium. We compare the experimental results to a theoretical model to understand the features required to observe a power law and to clarify the influence of external noise on spatial coherence in nonequilibrium phase transitions. Our results indicate that Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless-like phase order survives in open-dissipative systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
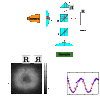

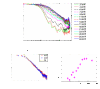


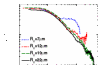
References
-
- Chaikin PM, Lubensky TC. Principles of Condensed Matter Physics. Cambridge Univ Press; 2000.
-
- Pitaevskii L, Stringari S. Bose-Einstein Condensation. Oxford Univ Press; 2003.
-
- Bloch I, Hänsch TW, Esslinger T. Measurement of the spatial coherence of a trapped Bose gas at the phase transition. Nature. 2000;403:166–170. - PubMed
-
- Hadzibabic Z, Dalibard J. Two-dimensional bose fluids: An atomic physics perspective. Rivista del Nuovo Cimento. 2011;34:389.
-
- Hohenberg PC. Existence of long-range order in one and two dimensions. Phys Rev. 1967;158:383–386.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

