Autoantibodies to αS1-casein are induced by breast-feeding
- PMID: 22496735
- PMCID: PMC3319542
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032716
Autoantibodies to αS1-casein are induced by breast-feeding
Abstract
Background: The generation of antibodies is impaired in newborns due to an immature immune system and reduced exposure to pathogens due to maternally derived antibodies and placental functions. During nursing, the immune system of newborns is challenged with multiple milk-derived proteins. Amongst them, caseins are the main constituent. In particular, human αS1-casein (CSN1S1) was recently shown to possess immunomodulatory properties. We were thus interested to determine if auto-antibodies to CSN1S1 are induced by breast-feeding and may be sustained into adulthood.
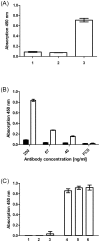
Methods: 62 sera of healthy adult individuals who were (n = 37) or were not (n = 25) breast-fed against human CSN1S1 were investigated by a new SD (surface display)-ELISA. For cross-checking, these sera were tested for anti Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) antibodies by a commercial ELISA.
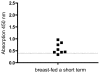
Results: IgG-antibodies were predominantly detected in individuals who had been nursed. At a cut-off value of 0.4, the SD-ELISA identified individuals with a history of having been breast-fed with a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 92%. Under these conditions, 35 out of 37 sera from healthy donors, who where breast-fed, reacted positively but only 5 sera of the 25 donors who were not breast-fed. The duration of breast-feeding was of no consequence to the antibody reaction as some healthy donors were only short term breast-fed (5 days minimum until 6 weeks maximum), but exhibited significant serum reaction against human CSN1S1 nonetheless.
Conclusion: We postulate that human CSN1S1 is an autoantigen. The antigenicity is orally determined, caused by breast-feeding, and sustained into adulthood.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


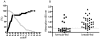


References
-
- Rejnek J, Prokesova L, Travnicek J. Early antibodies to human serum albumin formed in germfree piglets. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1974;19:520–524. - PubMed
-
- Chucri TM, Monteiro JM, Lima AR, Salvadori MLB, Kfoury JR, et al. A review of immune transfer by the placenta. Journal of Reproductive Immunology. 2010;87:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Vidor E. Vaccination of newborns against hepatitis a in the presence of maternally derived antibodies (2007). J Comp Pathol. 2007;137(Suppl 1):S42–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

