A bayesian model for exploiting application constraints to enable unsupervised training of a P300-based BCI
- PMID: 22496763
- PMCID: PMC3319551
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033758
A bayesian model for exploiting application constraints to enable unsupervised training of a P300-based BCI
Abstract
This work introduces a novel classifier for a P300-based speller, which, contrary to common methods, can be trained entirely unsupervisedly using an Expectation Maximization approach, eliminating the need for costly dataset collection or tedious calibration sessions. We use publicly available datasets for validation of our method and show that our unsupervised classifier performs competitively with supervised state-of-the-art spellers. Finally, we demonstrate the added value of our method in different experimental settings which reflect realistic usage situations of increasing difficulty and which would be difficult or impossible to tackle with existing supervised or adaptive methods.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



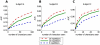
 that was used in the projection was trained unsupervisedly on the data.
that was used in the projection was trained unsupervisedly on the data.


References
-
- Vidal JJ. Toward direct brain-computer communication. Annual Review of Biophysics and Bioengineering. 1973;2:157–180. - PubMed
-
- Wolpaw JR, Birbaumer N, McFarland DJ, Pfurtscheller G, Vaughan TM. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2002;113:767–791. - PubMed
-
- Farwell L, Donchin E. Talking off the top of your head: toward a mental prosthesis utilizing event-related brain potentials. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology. 1988;70:510–523. - PubMed
-
- Vaughan T, McFarland D, Schalk G, Sarnacki W, Krusienski D, et al. The wadsworth BCI research and development program: at home with BCI. Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, IEEE Transactions on. 2006;14:229–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

