Sex- and age-related differences in bone microarchitecture in men relative to women assessed by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography
- PMID: 22496983
- PMCID: PMC3307008
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/129760
Sex- and age-related differences in bone microarchitecture in men relative to women assessed by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography
Abstract
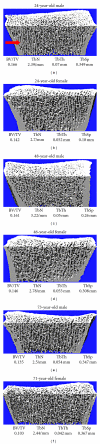
The trabecular and cortical compartments of bone each contributes to bone strength. Until recently, assessment of trabecular and cortical microstructure has required a bone biopsy. Now, trabecular and cortical microstructure of peripheral bone sites can be determined noninvasively using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT). Studies that have used HR-pQCT to evaluate cohorts of both men and women have provided novel insights into the changes in bone microarchitecture that occur with age between the sexes, which may help to explain the lower fracture incidence in older men relative to women. This review will highlight observations from these studies on both the sex- and age-related differences in trabecular and cortical microstructure that may underlie the differences in bone strength, and thereby fracture risk, between men and women.
Figures

References
-
- Muller R, Hildebrand T, Ruegsegger P. Non-invasive bone biopsy: a new method to analyse and display the three- dimensional structure of trabecular bone. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 1994;39(1):145–164. - PubMed
-
- Ulrich D, Rietbergen B, Laib A, Ruegsegger P. Mechanical analysis of bone and its microarchitecture based on in vivo voxel images. Technology and Health Care. 1998;6(5-6):421–427. - PubMed
-
- Seeman E, Delmas PD. Bone quality—the material and structural basis of bone strength and fragility. New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;354(21):2212–2261. - PubMed
-
- Müller R, Hildebrand T, Häuselmann HJ, Rüegsegger P. In vivo reproducibility of three-dimensional structural properties of noninvasive bone biopsies using 3D-pQCT. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 1996;11(11):1745–1750. - PubMed
-
- Laib A. Ridge number density: a new parameter for in vivo bone structure analysis. Bone. 1997;21(6):541–546. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

