Different roles of TM5, TM6, and ECL3 in the oligomerization and function of human ABCG2
- PMID: 22497316
- PMCID: PMC8276268
- DOI: 10.1021/bi300301a
Different roles of TM5, TM6, and ECL3 in the oligomerization and function of human ABCG2
Abstract
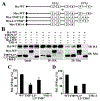
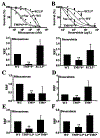
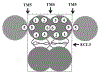
ABCG2 is a member of the ATP-binding cassette transporter superfamily, and its overexpression causes multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer chemotherapy. ABCG2 may also protect cancer stem cells by extruding cytotoxic materials. ABCG2 has previously been shown to exist as a high-order homo-oligomer consisting of possibly 8-12 subunits, and the oligomerization domain was mapped to the C-terminal domain, including TM5, ECL3, and TM6. In this study, we further investigate this domain in detail for the role of each segment in the oligomerization and drug transport function of ABCG2 using domain swapping and site-directed mutagenesis. We found that none of the three segments (TM5, TM6, and ECL3) is essential for the oligomerization activity of ABCG2 and that any one of these three segments in the full-length context is sufficient to support ABCG2 oligomerization. While TM5 plays an important role in the drug transport function of ABCG2, TM6 and ECL3 are replaceable. Thus, each segment in the TM5-ECL3-TM6 domain plays a distinctive role in the oligomerization and function of ABCG2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




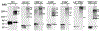
Similar articles
-
Oligomerization domain of the multidrug resistance-associated transporter ABCG2 and its dominant inhibitory activity.Cancer Res. 2007 May 1;67(9):4373-81. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3169. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17483351
-
Characterization of oligomeric human half-ABC transporter ATP-binding cassette G2.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 7;279(19):19781-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310785200. Epub 2004 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15001581
-
ABCG2 transports and transfers heme to albumin through its large extracellular loop.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 22;285(43):33123-33133. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.139170. Epub 2010 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20705604 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pharmacology of ABCG2 and its role in chemoresistance.Mol Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;84(5):655-69. doi: 10.1124/mol.113.088609. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Mol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24021215 Review.
-
Purification and structural analyses of ABCG2.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009 Jan 31;61(1):57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.07.004. Epub 2008 Dec 13. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009. PMID: 19124053 Review.
Cited by
-
The AKT inhibitor, MK-2206, attenuates ABCG2-mediated drug resistance in lung and colon cancer cells.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 13;14:1235285. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1235285. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37521473 Free PMC article.
-
Human ABCG2: structure, function, and its role in multidrug resistance.Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2012;3(1):1-27. Epub 2011 Mar 30. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22509477 Free PMC article.
-
Human bile acid transporter ASBT (SLC10A2) forms functional non-covalent homodimers and higher order oligomers.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 Mar;1860(3):645-653. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.11.016. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 29198943 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of residues in ABCG2 affecting protein trafficking and drug transport, using co-evolutionary analysis of ABCG sequences.Biosci Rep. 2015 Jul 17;35(4):e00241. doi: 10.1042/BSR20150150. Biosci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26294421 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of 14-3-3σ protein dimerization and function in drug and radiation resistance.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 1;288(44):31447-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.467753. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24043626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gottesman MM, Fojo T, and Bates SE (2002) Multidrug resistance in cancer: Role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 48–58. - PubMed
-
- Gottesman MM, Ambudkar SV, Ni B, Aran JM, Sugimoto Y, Cardarelli CO, and Pastan I (1994) Exploiting multidrug resistance to treat cancer. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol 59, 677–683. - PubMed
-
- Gillet JP, and Gottesman MM (2010) Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer. Methods Mol. Biol 596, 47–76. - PubMed
-
- Szakacs G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA, Booth-Genthe C, and Gottesman MM (2006) Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 5, 219–234. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JT (2007) Biochemistry and pharmacology of the human multidrug resistance gene product, ABCG2. Zhongnan Daxue Xuebao, Yixueban 32, 531–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

