Cationic PAMAM dendrimers disrupt key platelet functions
- PMID: 22497592
- PMCID: PMC3367133
- DOI: 10.1021/mp2006054
Cationic PAMAM dendrimers disrupt key platelet functions
Abstract
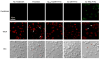
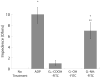
Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers have been proposed for a variety of biomedical applications and are increasingly studied as model nanomaterials for such use. The dendritic structure features both modular synthetic control of molecular size and shape and presentation of multiple equivalent terminal groups. These properties make PAMAM dendrimers highly functionalizable, versatile single-molecule nanoparticles with a high degree of consistency and low polydispersity. Recent nanotoxicological studies showed that intravenous administration of amine-terminated PAMAM dendrimers to mice was lethal, causing a disseminated intravascular coagulation-like condition. To elucidate the mechanisms underlying this coagulopathy, in vitro assessments of platelet functions in contact with PAMAM dendrimers were undertaken. This study demonstrates that cationic G7 PAMAM dendrimers activate platelets and dramatically alter their morphology. These changes to platelet morphology and activation state substantially altered platelet function, including increased aggregation and adherence to surfaces. Surprisingly, dendrimer exposure also attenuated platelet-dependent thrombin generation, indicating that not all platelet functions remained intact. These findings provide additional insight into PAMAM dendrimer effects on blood components and underscore the necessity for further research on the effects and mechanisms of PAMAM-specific and general nanoparticle toxicity in blood.
Figures
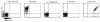
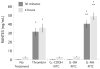

References
-
- Tomalia DA, Fréchet JMJ. Discovery of dendrimers and dendritic polymers: A brief historical perspective. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry. 2002;40:2719–2728.
-
- Radu DR, Lai CY, Jeftinija K, Rowe EW, Jeftinija S, Lin VSY. A Polyamidoamine Dendrimer- Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanosphere-Based Gene Transfection Reagent. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2004;126:13216–13217. - PubMed
-
- Bielinska AU, Yen A, Wu HL, Zahos KM, Sun R, Weiner ND, Baker JR, Jr, Roessler BJ. Application of membrane-based dendrimer/DNA complexes for solid phase transfection in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 2000;21:877–887. - PubMed
-
- Svenson S, Tomalia DA. Dendrimers in biomedical applications--reflections on the field. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:2106–29. - PubMed
-
- Esfand R, Tomalia DA. Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers: from biomimicry to drug delivery and biomedical applications. Drug Discov Today. 2001;6:427–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

