Forty-five years of schizophrenia trials in Italy: a survey
- PMID: 22497735
- PMCID: PMC3362749
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-13-35
Forty-five years of schizophrenia trials in Italy: a survey
Abstract
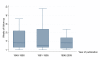
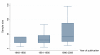
Background: Well-designed and properly executed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) provide the best evidence on the efficacy of healthcare interventions. Mental health has a strong tradition of using trial to evaluate treatments, but the translation of research to clinical practice is not always easy. Even well-conducted trials do not necessarily address the needs of every day care and trials can reflect local needs and the specific culture in which they are undertaken. Generalizing results to other contexts can become problematic but these trials may, nevertheless, be very helpful within their own context. Moreover, pathways for drug approval can be different depending on local regulatory agencies. Local trials are helpful for decision-making in the region from which they come, but should not be viewed in isolation. National quantity and quality of trials may vary across nations.The aim of this study is to quantify trialing activity in Italy from 1948 until 2009 and to describe characteristics of these trials. In addition, we evaluated change over time in three keys aspects: sample size, follow-up duration, and number of outcomes.
Methods: We used the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's register that contains 16,000 citations to 13,000 studies relating only to people with schizophrenia or schizophrenia-like illness. Randomized controlled trials and controlled clinical trials undertaken in Italy and involving pharmacological interventions were included.
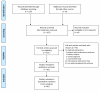
Results: The original search identified 155 records of potentially eligible studies, 74 of which were excluded because do not meet inclusion criteria. A total of 81 studies were included in the analysis. The majority of trials were conducted in north Italy, and published in international journals between 1981 and 1995. The majority of studies (52 out of 81) used standardized diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia disorder. They were defined as randomized and used blind methods to administer treatment. However, most failed to report detail regarding methodological procedures and it is difficult to ascertain which studies are associated with a low risk of bias.
Conclusions: Trials should be designed to address the needs of everyday care with the aim of following large samples of typical patients in the long term. The Italian tradition in the area of trialing treatments for people with schizophrenia is not as strong as in many other similar countries and Italy should be producing more, better, independent, and clinically relevant trials.
Figures

References
-
- Petrarca F. Rerum Senilium Libri. Liber XIV, Epistola 1. Letter to Boccaccio. 1364.
-
- Fioravanti L. Communication addressed to "Illustrissimo e Eccellentissimo Signor Al Protofisico Boldon e al Vicario di Giustizia. 1573.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

