Promoting crystallisation of the Salmonella enteritidis fimbriae 14 pilin SefD using deuterium oxide
- PMID: 22497887
- PMCID: PMC3522111
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.136
Promoting crystallisation of the Salmonella enteritidis fimbriae 14 pilin SefD using deuterium oxide
Abstract
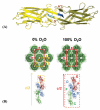
The use of heavy water (D(2)O) as a solvent is commonplace in many spectroscopic techniques for the study of biological macromolecules. A significant deuterium isotope effect exists where hydrogen-bonding is important, such as in protein stability, dynamics and assembly. Here we illustrate the use of D(2)O in additive screening for the production of reproducible diffraction-quality crystals for the Salmonella enteritidis fimbriae 14 (SEF14) putative tip adhesin, SefD.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Chayen NE, Saridakis E. Protein crystallization: from purified protein to diffraction-quality crystal. Nat Meth. 2008;5:147–153. - PubMed
-
- Derewenda ZS, Vekilov PG. Entropy and surface engineering in protein crystallization. Acta Crystallographica Section D. 2006;62:116–124. - PubMed
-
- Kim Y, Quartey P, Li H, Volkart L, Hatzos C, Chang C, Nocek B, Cuff M, Osipiuk J, Tan K, Fan Y, Bigelow L, Maltseva N, Wu R, Borovilos M, Duggan E, Zhou M, Binkowski TA, Zhang R.-g., Joachimiak A. Large-scale evaluation of protein reductive methylation for improving protein crystallization. Nat Meth. 2008;5:853–854. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

