Genome-wide analysis of mutations in mutant lineages selected following fast-neutron irradiation mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 22499668
- PMCID: PMC3396371
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.131474.111
Genome-wide analysis of mutations in mutant lineages selected following fast-neutron irradiation mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
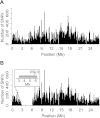
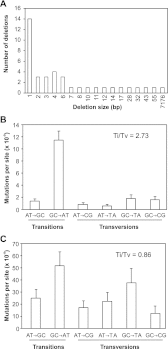
Ionizing radiation has long been known to induce heritable mutagenic change in DNA sequence. However, the genome-wide effect of radiation is not well understood. Here we report the molecular properties and frequency of mutations in phenotypically selected mutant lines isolated following exposure of the genetic model flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana to fast neutrons (FNs). Previous studies suggested that FNs predominantly induce deletions longer than a kilobase in A. thaliana. However, we found a higher frequency of single base substitution than deletion mutations. While the overall frequency and molecular spectrum of fast-neutron (FN)-induced single base substitutions differed substantially from those of "background" mutations arising spontaneously in laboratory-grown plants, G:C>A:T transitions were favored in both. We found that FN-induced G:C>A:T transitions were concentrated at pyrimidine dinucleotide sites, suggesting that FNs promote the formation of mutational covalent linkages between adjacent pyrimidine residues. In addition, we found that FNs induced more single base than large deletions, and that these single base deletions were possibly caused by replication slippage. Our observations provide an initial picture of the genome-wide molecular profile of mutations induced in A. thaliana by FN irradiation and are particularly informative of the nature and extent of genome-wide mutation in lines selected on the basis of mutant phenotypes from FN-mutagenized A. thaliana populations.
Figures

References
-
- Achard P, Cheng H, De Grauwe L, Decat J, Schoutteten H, Moritz T, Van Der Straeten D, Peng J, Harberd NP 2006. Integration of plant responses to environmentally activated phytohormonal signals. Science 311: 91–94 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad M, Jarillo JA, Smirnova O, Cashmore AR 1998. Cryptochrome blue-light photoreceptors of Arabidopsis implicated in phototropism. Nature 392: 720–723 - PubMed
-
- Ang LH, Chattopadhyay S, Wei N, Oyama T, Okada K, Batschauer A, Deng XW 1998. Molecular interaction between COP1 and HY5 defines a regulatory switch for light control of Arabidopsis development. Mol Cell 1: 213–222 - PubMed
-
- Bowman JL, Smyth DR, Meyerowitz EM 1991. Genetic interactions among floral homeotic genes of Arabidopsis. Development 112: 1–20 - PubMed
-
- Bruggemann E, Handwerger K, Essex C, Storz G 1996. Analysis of fast neutron-generated mutants at the Arabidopsis thaliana HY4 locus. Plant J 10: 755–760 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
