Somatic activation of AKT3 causes hemispheric developmental brain malformations
- PMID: 22500628
- PMCID: PMC3460551
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.010
Somatic activation of AKT3 causes hemispheric developmental brain malformations
Abstract
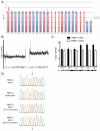
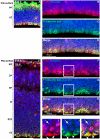
Hemimegalencephaly (HMG) is a developmental brain disorder characterized by an enlarged, malformed cerebral hemisphere, typically causing epilepsy that requires surgical resection. We studied resected HMG tissue to test whether the condition might reflect somatic mutations affecting genes critical to brain development. We found that two out of eight HMG samples showed trisomy of chromosome 1q, which encompasses many genes, including AKT3, a gene known to regulate brain size. A third case showed a known activating mutation in AKT3 (c.49G→A, creating p.E17K) that was not present in the patient's blood cells. Remarkably, the E17K mutation in AKT3 is exactly paralogous to E17K mutations in AKT1 and AKT2 recently discovered in somatic overgrowth syndromes. We show that AKT3 is the most abundant AKT paralog in the brain during neurogenesis and that phosphorylated AKT is abundant in cortical progenitor cells. Our data suggest that somatic mutations limited to the brain could represent an important cause of complex neurogenetic disease.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Arai Y, Edwards V, Becker LE. A comparison of cell phenotypes in hemimegalencephaly and tuberous sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 1999;98:407–413. - PubMed
-
- Ballif BC, Rosenfeld JA, Traylor R, Theisen A, Bader PI, Ladda RL, Sell SL, Steinraths M, Surti U, McGuire M, et al. High-resolution array CGH defines critical regions and candidate genes for microcephaly, abnormalities of the corpus callosum, and seizure phenotypes in patients with microdeletions of 1q43q44. Hum Genet. 2012;131:145–156. - PubMed
-
- Boland E, Clayton-Smith J, Woo VG, McKee S, Manson FD, Medne L, Zackai E, Swanson EA, Fitzpatrick D, Millen KJ, et al. Mapping of deletion and translocation breakpoints in 1q44 implicates the serine/threonine kinase AKT3 in postnatal microcephaly and agenesis of the corpus callosum. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81:292–303. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS35129/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 NS072192/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS032457/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P01 CA142536/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS079277/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD018655/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K99/R00 NS072192/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS035129/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23NS069784/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS069784/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS047213/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

