miRNAs and estrogen action
- PMID: 22503553
- PMCID: PMC3348384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.03.002
miRNAs and estrogen action
Abstract
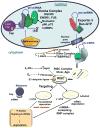
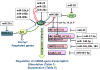
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short, noncoding RNAs that generally base-pair within the 3' untranslated region of target mRNAs causing translational inhibition and/or mRNA degradation. Estradiol (E(2)) and other estrogen receptor (ER) ligands suppress or stimulate miRNA expression in human breast cancer cells, endometrial cells, rat mammary gland, and mouse uterus, and post-translationally regulate protein expression. Aberrant miRNA expression is implicated in estrogen-related breast and endometrial cancers, and several miRNAs downregulate ERα. The role of estrogen-regulated miRNA expression, the target genes of these miRNAs, and the role of miRNAs in health and disease is a 'hot' area of research that will yield new insight into molecular mechanisms of estrogen action.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

