Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase mediates anhedonia and anxiety-like behaviors caused by peripheral lipopolysaccharide immune challenge
- PMID: 22504306
- PMCID: PMC3425718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.03.010
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase mediates anhedonia and anxiety-like behaviors caused by peripheral lipopolysaccharide immune challenge
Abstract
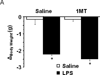
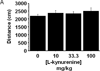
Upregulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) by proinflammatory cytokines has been implicated as a biological mediator of inflammation-related mood disorders. Clinical reports on this neuro-immune interaction remain correlative, while mechanism-centered preclinical experiments have focused on a relatively narrow, and somewhat controversial, survey of depression-like behaviors that include the forced swim and tail suspension tests. Here, we sought to determine whether peripheral immune challenge with Escherichia coli, lipopolysaccharides (LPS) precipitates the development of translationally relevant depression-like behaviors and to investigate the role of IDO in mediating these LPS-induced behaviors. Intraperitoneal injection of C57BL/6J mice with LPS resulted in a robust, but transient, reduction in exploratory locomotor activity (eLMA) that returned to near baseline levels by 24h. Sucrose preference, a preclinical correlate of anhedonia, was diminished by more than 20% in LPS-treated compared to saline-treated control mice, and LPS induced a significant increase in anxiety-like behavior at 24h that was independent eLMA. Pretreatment of mice with an IDO inhibitor, 1-methyltryptophan (1MT), ablated the anxiogenic effects of LPS, while having no impact on sickness associated changes in body weight or eLMA. Additionally, 1MT pretreatment attenuated the LPS-induced reduction in sucrose preference, which was also confirmed in IDO-1 null mice. Interestingly, acute systemic administration of l-kynurenine, the enzymatic product of IDO, precipitated an anhedonic and anxiogenic effect in naïve mice without effect on eLMA. In a preclinical model, these data implicate IDO as a pivotal mediator of LPS-induced depression- and anxiety-like behavior.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures













Similar articles
-
Central administration of lipopolysaccharide induces depressive-like behavior in vivo and activates brain indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase in murine organotypic hippocampal slice cultures.J Neuroinflammation. 2010 Aug 2;7:43. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-43. J Neuroinflammation. 2010. PMID: 20678226 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior is mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation in mice.Mol Psychiatry. 2009 May;14(5):511-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002148. Epub 2008 Jan 15. Mol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 18195714 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Host Defense Mechanisms against Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Anhedonic and Despair-Like Behaviors in Mice.Infect Immun. 2017 Mar 23;85(4):e00007-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00007-17. Print 2017 Apr. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28138019 Free PMC article.
-
The new '5-HT' hypothesis of depression: cell-mediated immune activation induces indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, which leads to lower plasma tryptophan and an increased synthesis of detrimental tryptophan catabolites (TRYCATs), both of which contribute to the onset of depression.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Apr 29;35(3):702-21. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.12.017. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21185346 Review.
-
Alcoholism and inflammation: neuroimmunology of behavioral and mood disorders.Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Jun;25 Suppl 1(0 1):S13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.12.013. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Brain Behav Immun. 2011. PMID: 21193024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low-Level Stress Induces Production of Neuroprotective Factors in Wild-Type but Not BDNF+/- Mice: Interleukin-10 and Kynurenic Acid.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Aug 1;19(3):pyv089. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv089. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26232788 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Systemic Inflammation Exacerbates Neurotoxicity in a Parkinson's Disease Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jan 13;2020:4807179. doi: 10.1155/2020/4807179. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32015787 Free PMC article.
-
Hirsutanol A Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Expression and Cytokines Production and Improves Endotoxemia-Induced Acute Sickness Behavior and Acute Lung Injury.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jun 17;17(6):360. doi: 10.3390/md17060360. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31213027 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs in treatment-resistant depression: a systematic review.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 May 10;51(1):638. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09554-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38727891
-
Depressive symptoms as a side effect of Interferon-α therapy induced by induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 20;6:29920. doi: 10.1038/srep29920. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27436416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassi GS, Kanashiro A, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sickness Behaviour Evaluated in Different Models of Anxiety and Innate Fear in Rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011 - PubMed
-
- Bonaccorso S, Marino V, et al. Increased depressive ratings in patients with hepatitis C receiving interferon-alpha-based immunotherapy are related to interferon-alpha-induced changes in the serotonergic system. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2002;22(1):86–90. - PubMed
-
- Capuron L, Miller AH. Cytokines and psychopathology: lessons from interferon-alpha. Biol Psychiatry. 2004;56(11):819–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

