The location of splenic NKT cells favours their rapid activation by blood-borne antigen
- PMID: 22505026
- PMCID: PMC3364740
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.87
The location of splenic NKT cells favours their rapid activation by blood-borne antigen
Abstract
Natural killer T (NKT) cells play an important role in mounting protective responses to blood-borne infections. However, though the spleen is the largest blood filter in the body, the distribution and dynamics of NKT cells within this organ are not well characterized. Here we show that the majority of NKT cells patrol around the marginal zone (MZ) and red pulp (RP) of the spleen. In response to lipid antigen, these NKT cells become arrested and rapidly produce cytokines, while the small proportion of NKT cells located in the white pulp (WP) exhibit limited activation. Importantly, disruption of the splenic MZ by chemical or genetic approaches results in a severe reduction in NKT cell activation indicating the need of cooperation between both MZ macrophages and dendritic cells for efficient NKT cell responses. Thus, the location of splenic NKT cells in the MZ and RP facilitates their access to blood-borne antigen and enables the rapid initiation of protective immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
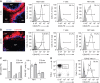

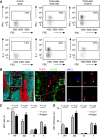
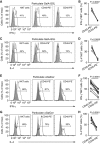
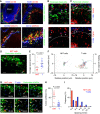

 ) incubated with αGalCer particles previous to co-culture with DN32.D3 NKT cells. Secretion of IL-2 into the culture medium by DN32.D3 cells was measured as a read-out for lipid presentation.
) incubated with αGalCer particles previous to co-culture with DN32.D3 NKT cells. Secretion of IL-2 into the culture medium by DN32.D3 cells was measured as a read-out for lipid presentation.
References
-
- Aichele P, Zinke J, Grode L, Schwendener RA, Kaufmann SHE, Seiler P (2003) Macrophages of the splenic marginal zone are essential for trapping of blood-borne particulate antigen but dispensable for induction of specific T cell responses. J Immunol 171: 1148–1155 - PubMed
-
- Andrews DM, Farrell HE, Densley EH, Scalzo AA, Shellam GR, Degli-Esposti MA (2001) NK1.1+ cells and murine cytomegalovirus infection: what happens in situ? J Immunol 166: 1796–1802 - PubMed
-
- Aoshi T, Zinselmeyer BH, Konjufca V, Lynch JN, Zhang X, Koide Y, Miller MJ (2008) Bacterial entry to the splenic white pulp initiates antigen presentation to CD8+ T cells. Immunity 29: 476–486 - PubMed
-
- Backer R, Schwandt T, Greuter M, Oosting M, Jungerkes F, Tuting T, Boon L, O’toole T, Kraal G, Limmer A, Den Haan JMM (2010) Effective collaboration between marginal metallophilic macrophages and CD8+ dendritic cells in the generation of cytotoxic T cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107: 216–221 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

