The biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance gene ndvB is important for expression of ethanol oxidation genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms
- PMID: 22505683
- PMCID: PMC3370848
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.06178-11
The biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance gene ndvB is important for expression of ethanol oxidation genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms
Abstract
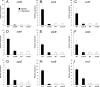
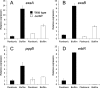
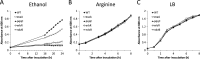
Bacteria growing in biofilms are responsible for a large number of persistent infections and are often more resistant to antibiotics than are free-floating bacteria. In a previous study, we identified a Pseudomonas aeruginosa gene, ndvB, which is important for the formation of periplasmic glucans. We established that these glucans function in biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance by sequestering antibiotic molecules away from their cellular targets. In this study, we investigate another function of ndvB in biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance. DNA microarray analysis identified 24 genes that were responsive to the presence of ndvB. A subset of 20 genes, including 8 ethanol oxidation genes (ercS', erbR, exaA, exaB, eraR, pqqB, pqqC, and pqqE), was highly expressed in wild-type biofilm cells but not in ΔndvB biofilms, while 4 genes displayed the reciprocal expression pattern. Using quantitative real-time PCR, we confirmed the ndvB-dependent expression of the ethanol oxidation genes and additionally demonstrated that these genes were more highly expressed in biofilms than in planktonic cultures. Expression of erbR in ΔndvB biofilms was restored after the treatment of the biofilm with periplasmic extracts derived from wild-type biofilm cells. Inactivation of ethanol oxidation genes increased the sensitivity of biofilms to tobramycin. Together, these results reveal that ndvB affects the expression of multiple genes in biofilms and that ethanol oxidation genes are linked to biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance.
Figures

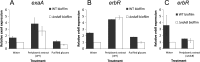
References
-
- Blatny JM, Brautaset T, Winther-Larsen HC, Karunakaran P, Valla S. 1997. Improved broad-host-range RK2 vectors useful for high and low regulated gene expression levels in Gram-negative bacteria. Plasmid 38:35–51 - PubMed
-
- CLSI 2009. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically. Approved standard—eighth edition. CLSI document M07-A8Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
-
- Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP. 1999. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322 - PubMed
-
- Development Core Team R 2006. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria: http://www.R-project.org
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

