Distinctive roles for amygdalar CREB in reconsolidation and extinction of fear memory
- PMID: 22505719
- PMCID: PMC3348518
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.025783.112
Distinctive roles for amygdalar CREB in reconsolidation and extinction of fear memory
Abstract
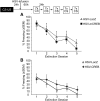
Cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB) plays a critical role in fear memory formation. Here we determined the role of CREB selectively within the amygdala in reconsolidation and extinction of auditory fear. Viral overexpression of the inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER) or the dominant-negative mCREB, specifically within the lateral amygdala disrupted reconsolidation of auditory fear memories. In contrast, manipulations of CREB in the amygdala did not modify extinction of fear. These findings suggest that the role of CREB in modulation of memory after retrieval is dynamic and that CREB activity in the basolateral amygdala is involved in fear memory reconsolidation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brain region-specific gene expression activation required for reconsolidation and extinction of contextual fear memory.J Neurosci. 2009 Jan 14;29(2):402-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4639-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19144840 Free PMC article.
-
Extinction, applied after retrieval of auditory fear memory, selectively increases zinc-finger protein 268 and phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 expression in prefrontal cortex and lateral amygdala.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Nov;115:78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.08.015. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 25196703
-
Differential role of Rac in the basolateral amygdala and cornu ammonis 1 in the reconsolidation of auditory and contextual Pavlovian fear memory in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Aug;231(15):2909-19. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3462-0. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24553575
-
Erasing fear memories with extinction training.J Neurosci. 2010 Nov 10;30(45):14993-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4268-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21068303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain sites involved in fear memory reconsolidation and extinction of rodents.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Jun;53:160-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 25887284 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurobiological dissociation of retrieval and reconsolidation of cocaine-associated memory.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 16;33(3):1271-81a. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3463-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23325262 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition after retrieval switches the memory fate favoring extinction instead of reconsolidation.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 21;13(1):20384. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47717-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37990053 Free PMC article.
-
Unconditioned- and Conditioned- Stimuli Induce Differential Memory Reconsolidation and β-AR-Dependent CREB Activation.Front Neural Circuits. 2017 Aug 10;11:53. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2017.00053. eCollection 2017. Front Neural Circuits. 2017. PMID: 28848401 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Model of Weak Depression Exhibiting Suppressed cAMP Signaling in the Amygdala, Lower Lipid Catabolism in Liver, and Correlated Gut Microbiota.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 May 19;16:841450. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.841450. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35928791 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomic Analysis Reveals a Novel Mechanism of CaMKIIα Regulation Inversely Induced by Cocaine Memory Extinction versus Reconsolidation.J Neurosci. 2016 Jul 20;36(29):7613-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1108-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27445140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bahar A, Dorfman N, Dudai Y 2004. Amygdalar circuits required for either consolidation or extinction of taste aversion memory are not required for reconsolidation. Eur J Neurosci 19: 1115–1118 - PubMed
-
- Bourtchuladze R, Frenguelli B, Blendy J, Cioffi D, Schutz G, Silva AJ 1994. Deficient long-term memory in mice with a targeted mutation of the cAMP-responsive element-binding protein. Cell 79: 59–68 - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME 1993. Context, time, and memory retrieval in the interference paradigms of Pavlovian learning. Psychol Bull 114: 80–99 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
