The effects of disinfectants on dimensional accuracy and surface quality of impression materials and gypsum casts
- PMID: 22505972
- PMCID: PMC3318858
- DOI: 10.4021/jocmr2009.04.1235
The effects of disinfectants on dimensional accuracy and surface quality of impression materials and gypsum casts
Abstract
Background: The study aimed to evaluating the effect of disinfecting impression materials on the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the resulting casts.
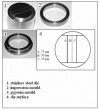
Methods: Impressions of a steel die constructed according to ANSI/ADA specification No.18 were made with each of alginate, addition cured silicone, condensation cured silicone and zinc oxide eugenol paste, and disinfected consequently by each of 0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate, 1% sodium hypochlorite, 2% gluteraldehyde for 5 minutes, and 0.5% sodium hypochlorite for 10 minutes. Dimensions of the disinfected impressions and their resultant casts were measured using a computerized digital caliper, and the dimensional changes were calculated. Reproduction of detail and surface quality of the resultant casts were assessed by grading casts surfaces according to a specific scoring system.
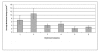
Results: The 0.5% sodium hypochlorite was found to produce the least dimensional changes in all the impression materials. Corsodyl produced the maximum changes in both alginate and zinc-oxide eugenol while addition-cured silicon was most affected by Gluteraldehyde and condensation-cured silicon was most affected by Hexana. The dimensional changes, however, were minimal and clinically insignificant. Addition-cured silicon showed the best surface quality and dimensional stability followed by condensation-cured silicon. Alginate and zinc-oxide eugenol had poorer surface quality and were affected to a higher extent by the disinfection procedures.
Conclusions: The results were comparable with the standard specifications for dimensional stability. Recommendations were made for the use of 10 minutes immersion in 0.5% sodium hypochlorite as the most appropriate disinfection protocol to the investigated impression materials.
Keywords: Disinfectants; Gypsum casts; Impressions; Alginate; Addition-cured silicone; Sodium hypochlorite.
Figures





References
-
- Leung RL, Schonfeld SE. Gypsum casts as a potential source of microbial cross-contamination. J Prosthet Dent. 1983;49(2):210–211. - PubMed
-
- Fabiani L, Mosca G, Giuliani AR. Hygiene in dental practices. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2006;7(2):93–97. - PubMed
-
- Infection control recommendations for the dental office and the dental laboratory. ADA Council on Scientific Affairs and ADA Council on Dental Practice. J Am Dent Assoc. 1996;127(5):672–680. - PubMed
-
- Kohn WG, Collins AS, Cleveland JL, Harte JA, Eklund KJ, Malvitz DM. Guidelines for infection control in dental health-care settings--2003. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2003;52(RR-17):1–61. - PubMed
-
- Taylor RL, Wright PS, Maryan C. Disinfection procedures: their effect on the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of irreversible hydrocolloid impression materials and gypsum casts. Dent Mater. 2002;18(2):103–110. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
