Nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia in cancer therapy
- PMID: 22506095
- PMCID: PMC3323111
- DOI: 10.4155/tde.11.72
Nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia in cancer therapy
Abstract
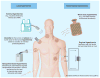
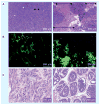
A small rise in tumor temperature (hyperthermia) makes cancer cells more susceptible to radiation and chemotherapy. The means of achieving this is not trivial, and traditional methods have certain drawbacks. Loading tumors with systematically asministered energy-transducing nanoparticles can circumvent several of the obstacles to achieve tumor hyperthermia. However, nanoparticles also face unique challenges prior to clinical implementation. This article summarizes the state-of-the-art current technology and discusses the advantages and challenges of the three major nanoparticle formulations in focus: gold nanoshells and nanorods, superparamagnetic iron oxide particles and carbon nanotubes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Next-generation superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for cancer theranostics.Drug Discov Today. 2017 Sep;22(9):1421-1429. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Drug Discov Today. 2017. PMID: 28454771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational nanomedicine: modeling of nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermal cancer therapy.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2013 Aug;8(8):1323-33. doi: 10.2217/nnm.13.117. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2013. PMID: 23914967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for tumor-targeted therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011 Feb;11(2):184-9. doi: 10.2174/156800911794328475. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21158723 Review.
-
Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia: a new frontier in biology and medicine?Int J Hyperthermia. 2013 Dec;29(8):703-5. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2013.857434. Int J Hyperthermia. 2013. PMID: 24219798 No abstract available.
-
Hyperthermia using nanoparticles--Promises and pitfalls.Int J Hyperthermia. 2016;32(1):76-88. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2015.1120889. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Int J Hyperthermia. 2016. PMID: 26757879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous hyperthermia-chemotherapy with controlled drug delivery using single-drug nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 22;6:24629. doi: 10.1038/srep24629. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27103308 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of drugs, proteins, and nucleic acids using inorganic nanoparticles.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;156:188-213. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.020. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 32610061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Finite Element Analysis of Silver Nanorods, Spheres, Ellipsoids and Core-Shell Structures for Hyperthermia Treatment of Cancer.Materials (Basel). 2022 Feb 26;15(5):1786. doi: 10.3390/ma15051786. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35269017 Free PMC article.
-
Photothermal Therapy as Adjuvant to Surgery in an Orthotopic Mouse Model of Human Fibrosarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 20;13(22):5820. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225820. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830974 Free PMC article.
-
Polylysine as a functional biopolymer to couple gold nanorods to tumor-tropic cells.J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 May 31;16(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0377-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29855304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedenthal E, Mendecki J, Botstein C, Sterzer F, Nowogrodzki M, Paglione R. Some practical considerations for the use of localized hyperthermia in the treatment of cancer. J Microw Power. 1981;16(2):199–204. - PubMed
-
- Lele PP. Induction of deep, local hyperthermia by ultrasound and electromagnetic fields: problems and choices. Radiat Environ Biophys. 1980;17(3):205–217. - PubMed
-
- Magin RL, Johnson RK. Effects of local tumor hyperthermia on the growth of solid mouse tumors. Cancer Res. 1979;39(11):4534–4539. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Hahn EW, Ahmed SA. Combination hyperthermia and radiation therapy for malignant melanoma. Cancer. 1982;50(3):478–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
