Nerve conduction study of the superficial peroneal sensory distal branches in koreans
- PMID: 22506172
- PMCID: PMC3309246
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2011.35.4.548
Nerve conduction study of the superficial peroneal sensory distal branches in koreans
Abstract
Objective: To perform nerve conduction studies of the four branches of the superficial peroneal nerves to determine normal values and anatomic variations in Koreans.
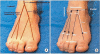
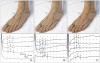
Method: Antidromic sensory nerve conduction studies of the four distal branches were performed on 70 healthy subjects (100 feet). We applied electrical stimulation at the midpoint of medial and lateral malleoli for the medial dorsal cutaneous nerve (MDCN), and at the lateral 1/4 point between the medial and lateral malleoli for the 2 branches of the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve (IDCN).
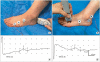
Results: Reference values (mean±SD) of the onset/ peak latency (ms)/ sensory action potential amplitude (µV) for the two branches of the MDCN and for the first branch of the IDCN were 2.2±0.3/2.9±0.3/9.2±3.1, 2.2±0.3/2.8±0.3/9.1±3.0 and 2.3±0.4/2.9±0.3/8.5±2.8, respectively. For the second IDCN branch, the reference values were 2.3±0.4/3.0±0.4/7.1±2.6 but anomalous sural innervation was also found. Three types of IDCN innervations to the fourth interdigital web space were detected. In type I, the fourth interdigital webspace was innervated solely by the IDCN, whereas in type II, it was innervated by both the IDCN and distal sural nerve. In type III, it was solely innervated by the distal sural nerve.
Conclusion: The results of this study show the reference values of the distal sensory branches of the superficial peroneal nerve, and provide information on the variant innervations to the fourth interdigital web space.
Keywords: Innervations; Reference values; Sensory nerve; Superficial peroneal; Variant.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination and classification of cutaneous innervation of the dorsum of the foot in foetal cadavers.Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2018;77(4):698-702. doi: 10.5603/FM.a2018.0020. Epub 2018 Mar 3. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2018. PMID: 29500895
-
Variations in the distal branches of the superficial fibular sensory nerve.Muscle Nerve. 2017 Jan;55(1):74-76. doi: 10.1002/mus.25196. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Muscle Nerve. 2017. PMID: 27214730
-
Electrophysiological contribution of both sensory branches of the superficial peroneal nerve in the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy.Neurodiagn J. 2012 Sep;52(3):291-300. Neurodiagn J. 2012. PMID: 23019766
-
Variations in the compartmental location of the superficial fibular nerve: a cadaveric study with meta-analysis.Surg Radiol Anat. 2022 Nov;44(11):1431-1437. doi: 10.1007/s00276-022-03041-3. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Surg Radiol Anat. 2022. PMID: 36344693 Review.
-
The communicating branches between the sural and superficial peroneal nerves in the foot: a review of 55 cases.Surg Radiol Anat. 2004 Dec;26(6):447-52. doi: 10.1007/s00276-004-0264-9. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004. PMID: 15300414 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory effect of IL-17 on neural stem cell proliferation and neural cell differentiation.BMC Immunol. 2013 Apr 23;14:20. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-14-20. BMC Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23617463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braddom RL, Hollis JB, Castell DO. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a correlation of nerve conduction studies and clinical findings. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1977;58:308–313. - PubMed
-
- Celiker R, Basgze O, Bayraktar M. Early detection of neurological involvement in diabetes mellitus. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1996;36:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Ryu GH, Nam KY, Jun JY, Sim YJ, Choi JH, Kwon BS, Park JW, Lim HS. New method and usefullness of study on sensory nerve conduction of lateral sural cutaneous Nerve. J Korean Acad Rehab Med. 2008;32:300–304.
-
- Uluc K, Isak B, Borucu D, Temucin CM, Cetinkaya Y, Koytak PK, Tanridag T, Us O. Medial plantar and dorsal sural nerve conduction studies increase the sensitivity in the detection of neuropathy in diabetic patients. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008;119:880–885. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

