Efficacy of ultrasonography-guided injections in patients with facet syndrome of the low lumbar spine
- PMID: 22506237
- PMCID: PMC3309334
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2012.36.1.66
Efficacy of ultrasonography-guided injections in patients with facet syndrome of the low lumbar spine
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the efficacy of ultrasonography (US)-guided injections in patients with low lumbar facet syndrome, compared with that in patients who received fluoroscopy (FS)-guided injections.
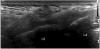
Method: Fifty-seven subjects with facet syndrome of the lumbar spine of the L4-5 and L5-S1 levels were randomly divided into two groups to receive intraarticular injections into the facet joint. One group received FS-guided facet joint injections and the other group received US-guided facet joint injections. Treatment effectiveness was assessed using a visual analogue scale (VAS), physician's and patient's global assessment (PhyGA, PaGA), and the modified Oswestry Disability Index (MODI). All parameters were evaluated four times: before injections, and at a week, a month, and three months after injections. We also measured, in both groups, how long it took to complete the whole procedure.
Results: Each group showed significant improvement from the facet joint injections on the VAS, PhyGA, PaGA, and MODI (p<0.05). However at a week, a month, and three months after injections, no significant differences were observed between the groups with regard to VAS, PhyGA, PaGA, and MODI (p>0.05). Statistically significant differences in procedure time were observed between groups (FS: 248.7±6.5 sec; US: 263.4±5.9 sec; p=0.023).
Conclusion: US-guided injections in patients with lumbar facet syndrome are as effective as FS-guided injections for pain relief and improving activities of daily living.
Keywords: Intraarticular injections; Low-back pain; Ultrasonography; Zygapophysial joint.
Figures

References
-
- Boswell MV, Colson JD, Spillane WF. Therapeutic facet joint interventions in chronic spinal pain: a systematic review of effectiveness and complications. Pain Physician. 2005;8:101–114. - PubMed
-
- Sehgal N, Shah RV, McKenzie-Brown AM, Everett CR. Diagnostic utility of facet (zygapophysial) joint injections in chronic spinal pain: a systematic review of evidence. Pain Physician. 2005;8:211–224. - PubMed
-
- Joy H, Ha SK, Kim SH, Lim DJ, Park JY, Suh JK. Prognostic factors of percutaneous radiofrequency neurotomy on the posterior primary ramus. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2003;33:51–55.
-
- Bogduk N. International Spinal Injections Society guidelines for the performance of spinal injections procedures. Part I: Zygapophysial joint blocks. Clin J Pain. 1997;13:285–302. - PubMed
-
- Greher M, Kirchmair L, Enna B, Kovacs P, Gustorff B, Kapral S, Moriggl B. Ultrasound-guided lumbar facet nerve block: accuracy of a new technique confirmed by computed tomography. Anesthesiology. 2004;101:1195–1200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

