Solution structure studies of monomeric human TIP47/perilipin-3 reveal a highly extended conformation
- PMID: 22508559
- PMCID: PMC3393791
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.24095
Solution structure studies of monomeric human TIP47/perilipin-3 reveal a highly extended conformation
Abstract
Tail-interacting protein of 47 kDa (TIP47) has two putative functions: lipid biogenesis and mannose 6-phosphate receptor recycling. Progress in understanding the molecular details of these two functions has been hampered by the lack of structural data on TIP47, with a crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of the mouse homolog constituting the only structural data in the literature so far. Our studies have first provided a strategy to obtain pure monodisperse preparations of the full-length TIP47/perilipin-3 protein, as well as a series of N-terminal truncation mutants with no exogenous sequences. These constructs have then enabled us to obtain the first structural characterization of the full-length protein in solution. Our work demonstrates that the N-terminal region of TIP47/perilipin-3, in contrast to the largely helical C-terminal region, is predominantly β-structure with turns and bends. Moreover, we show that full-length TIP47/perilipin-3 adopts an extended conformation in solution, with considerable spatial separation of the N- and C-termini that would likely translate into a separation of functional domains.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
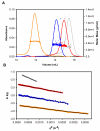
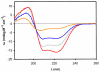
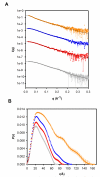

Similar articles
-
Identification of residues in TIP47 essential for Rab9 binding.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 May 28;99(11):7450-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.112198799. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12032303 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembly is important for TIP47 function in mannose 6-phosphate receptor transport.Traffic. 2003 Jan;4(1):18-25. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2003.40104.x. Traffic. 2003. PMID: 12535272
-
Structure of a lipid droplet protein; the PAT family member TIP47.Structure. 2004 Jul;12(7):1199-207. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2004.04.021. Structure. 2004. PMID: 15242596
-
[The double-play of PP17/TIP47].Med Sci (Paris). 2004 Nov;20(11):1020-5. doi: 10.1051/medsci/200420111020. Med Sci (Paris). 2004. PMID: 15525499 Review. French.
-
Disorder in milk proteins: adipophilin and TIP47, important constituents of the milk fat globule membrane.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020 Mar;38(4):1214-1229. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2019.1592027. Epub 2019 Mar 21. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020. PMID: 30896308 Review.
Cited by
-
Binding of perilipin 3 to membranes containing diacylglycerol is mediated by conserved residues within its PAT domain.J Biol Chem. 2023 Dec;299(12):105384. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105384. Epub 2023 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37898398 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional assessment of perilipin 2 lipid binding domain(s).Biochemistry. 2014 Nov 18;53(45):7051-66. doi: 10.1021/bi500918m. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25338003 Free PMC article.
-
Rab proteins and the compartmentalization of the endosomal system.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Oct 23;6(11):a022616. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022616. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25341920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface tension-driven sorting of human perilipins on lipid droplets.J Cell Biol. 2024 Dec 2;223(12):e202403064. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202403064. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39297796 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic over-nutrition and dysregulation of GSK3 in diseases.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016 Aug 4;13:49. doi: 10.1186/s12986-016-0108-8. eCollection 2016. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016. PMID: 27493677 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brasaemle DL. Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet proteins: stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:2547–2559. - PubMed
-
- Bauby H, Lopez-Verges S, Hoeffel G, Delcroix-Genete D, Janvier K, Mammano F, Hosmalin A, Berlioz-Torrent C. TIP47 is required for the production of infectious HIV-1 particles from primary macrophages. Traffic. 2010;11:455–467. - PubMed
-
- Bohn H, Kraus W, Winckler W. Purification and characterization of two new soluble placental tissue proteins (PP13 and PP17) Oncodev Biol Med. 1983;4:343–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

