A pilot study of lis-dexamfetamine dimesylate (LDX/SPD489) to facilitate smoking cessation in nicotine-dependent adults with ADHD
- PMID: 22508760
- PMCID: PMC3421044
- DOI: 10.1177/1087054712440320
A pilot study of lis-dexamfetamine dimesylate (LDX/SPD489) to facilitate smoking cessation in nicotine-dependent adults with ADHD
Abstract
Objective: The goal of this study was to assess the efficacy and tolerability of lis-dexamfetamine dimesylate (LDX) as an adjunct to nicotine replacement therapy in adult smokers with ADHD who were undergoing a quit attempt.
Methods: Thirty-two regular adult smokers with ADHD were randomized to receive LDX (n = 17) or placebo (n = 15) in addition to nicotine patch concurrent with a quit attempt.
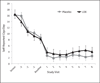
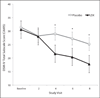
Results: There were no differences between smokers assigned to LDX versus placebo in any smoking outcomes. Participants treated with LDX demonstrated significant reductions in self-reported and clinician-rated ADHD symptoms. LDX was well tolerated in smokers attempting to quit.
Discussion: In general, LDX does not facilitate smoking cessation in adults with ADHD more than does placebo, though both groups significantly reduced smoking. LDX demonstrated efficacy for reducing ADHD symptoms in adult smokers engaging in a quit attempt.
Keywords: adult ADHD; lis-dexamfetamine dimesylate; smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: During the period of the study, the following disclosures are noted. Dr. Kollins received research support and/or consulting fees fro, Shire Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, Addrenex Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc., and NIDA/NIH. Dr. McClernon received research support from Philip Morris USA and NIDA/NIH. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder previously treated with amphetamines: analyses from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled titration study.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012 Dec 19;13:18. doi: 10.1186/2050-6511-13-18. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 23254273 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (NRP-104) in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, forced-dose, parallel-group study.Clin Ther. 2007 Mar;29(3):450-63. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(07)80083-x. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 17577466 Clinical Trial.
-
Self-Reported quality of life in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and executive function impairment treated with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate: a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study.BMC Psychiatry. 2013 Oct 9;13:253. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-253. BMC Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24106804 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and safety profile of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate, a prodrug of d-amphetamine, for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adults.Clin Ther. 2009 Jan;31(1):142-76. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.01.015. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19243715 Review.
-
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate: a new option in stimulant treatment for ADHD.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010 Dec;11(17):2907-13. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2010.531009. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20979573 Review.
Cited by
-
ADHD, Smoking Withdrawal, and Inhibitory Control: Results of a Neuroimaging Study with Methylphenidate Challenge.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Mar;43(4):851-858. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.248. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29052617 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of smoking abstinence on smoking-reinforced responding, withdrawal, and cognition in adults with and without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 May;227(1):19-30. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2937-0. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23247366 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 21;15(10):e0240584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240584. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33085721 Free PMC article.
-
Amphetamines for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 9;8(8):CD007813. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007813.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30091808 Free PMC article.
-
Methylphenidate does not influence smoking-reinforced responding or attentional performance in adult smokers with and without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013 Oct;21(5):375-84. doi: 10.1037/a0033851. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24099358 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Adler LA, Goodman DW, Kollins SH, Weisler RH, Krishnan S, Zhang Y, Biederman J. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2008;69:1364–1373. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&;db=PubMed&do.... - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: Author; 1994.
-
- Brackenridge R, McKenzie K, Murray GC, Quigley A. An examination of the effects of stimulant medication on response inhibition: A comparison between children with and without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Research in Developmental Disabilities. 2011;32:2797–2804. - PubMed
-
- Brown TE, Brams M, Gasior M, Adeyi B, Babcock T, Dirks BT. Clinical utility of ADHD symptom thresholds to assess normalization of executive function with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate treatment in adults. Current Medical Research & Opinion. 2011;27(Suppl. 2):23–33. - PubMed
-
- Bullen C, Howe C, Lin RB, Grigg M, Laugesen M, McRobbie H, Rodgers A. Pre-cessation nicotine replacement therapy: Pragmatic randomized trial. Addiction. 2010;105:1474–1483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

