Comparison of PPIs and H2-receptor antagonists plus prokinetics for dysmotility-like dyspepsia
- PMID: 22509084
- PMCID: PMC3319948
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i13.1517
Comparison of PPIs and H2-receptor antagonists plus prokinetics for dysmotility-like dyspepsia
Abstract
Aim: To compare efficacy of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) with H(2)-receptor antagonists (H(2)RAs) plus prokinetics (Proks) for dysmotility-like symptoms in functional dyspepsia (FD).
Methods: Subjects were randomized to receive open-label treatment with either rabeprazole 10 mg od (n = 57) or famotidine 10 mg bid plus mosapride 5 mg tid (n = 57) for 4 wk. The primary efficacy endpoint was change (%) from baseline in total dysmotility-like dyspepsia symptom score. The secondary efficacy endpoint was patient satisfaction with treatment.
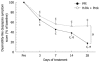
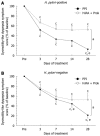
Results: The improvement in dysmotility-like dyspepsia symptom score on day 28 was significantly greater in the rabeprazole group (22.5% ± 29.2% of baseline) than the famotidine + mosapride group (53.2% ± 58.6% of baseline, P < 0.0001). The superior benefit of rabeprazole treatment after 28 d was consistent regardless of Helicobacter pylori status. Significantly more subjects in the rabeprazole group were satisfied or very satisfied with treatment on day 28 than in the famotidine + mosapride group (87.7% vs 59.6%, P = 0.0012). Rabeprazole therapy was the only significant predictor of treatment response (P < 0.0001), defined as a total symptom score improvement ≥ 50%.
Conclusion: PPI monotherapy improves dysmotility-like symptoms significantly better than H(2)RAs plus Proks, and should be the treatment of first choice for Japanese FD.
Keywords: Dysmotility; Functional dyspepsia; H2-receptor antagonist; Prokinetics; Proton pump inhibitor.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Observational comparative trial of the efficacy of proton pump inhibitors versus histamine-2 receptor antagonists for uninvestigated dyspepsia.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 May;25 Suppl 1:S122-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06218.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20586853
-
Effects of famotidine, mosapride and tandospirone for treatment of functional dyspepsia.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Jun;21 Suppl 2:37-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02472.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15943845 Clinical Trial.
-
Proton pump inhibitor versus prokinetic therapy in patients with functional dyspepsia: is therapeutic response predicted by Rome III subgroups?J Gastroenterol. 2011 Feb;46(2):183-90. doi: 10.1007/s00535-010-0334-1. Epub 2010 Oct 19. J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 20957498 Clinical Trial.
-
Review article: current treatment options and management of functional dyspepsia.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Jul;36(1):3-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2012.05128.x. Epub 2012 May 16. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22591037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Dec;11(51):iii-iv, 1-164. doi: 10.3310/hta11510. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 18021578 Review.
Cited by
-
Current management strategies and emerging treatments for functional dyspepsia.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Mar;10(3):187-94. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.11. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23381190 Review.
-
Disorders of gastrointestinal hypomotility.F1000Res. 2016 Aug 1;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-1897. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.8658.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27583135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical characteristics and effectiveness of lansoprazole in Japanese patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease and dyspepsia.J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr;49(4):628-37. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0812-3. Epub 2013 May 8. J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 23653056 Clinical Trial.
-
Proton pump inhibitors for functional dyspepsia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 8;3(3):CD011194. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011194.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 21;11:CD011194. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011194.pub3. PMID: 28271513 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Combined contributions of cytochrome P450s (CYPs) and non-enzymatic metabolism in the in vitro biotransformation of anaprazole, a novel proton pump inhibitor.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Aug;396(8):1759-1771. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02415-7. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36847804
References
-
- Tack J, Talley NJ, Camilleri M, Holtmann G, Hu P, Malagelada JR, Stanghellini V. Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1466–1479. - PubMed
-
- Tack J, Bisschops R, Sarnelli G. Pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1239–1255. - PubMed
-
- Nyrén O, Adami HO, Gustavsson S, Lindgren PG, Lööf L, Nyberg A. The “epigastric distress syndrome”. A possible disease entity identified by history and endoscopy in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987;9:303–309. - PubMed
-
- Talley NJ, Meineche-Schmidt V, Paré P, Duckworth M, Räisänen P, Pap A, Kordecki H, Schmid V. Efficacy of omeprazole in functional dyspepsia: double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials (the Bond and Opera studies) Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1998;12:1055–1065. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

