Association of insulin-like growth factor-1 polymorphisms with high myopia in the Chinese population
- PMID: 22509095
- PMCID: PMC3324364
Association of insulin-like growth factor-1 polymorphisms with high myopia in the Chinese population
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine whether genetic variants in the insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) gene were associated with high myopia in the Chinese population.
Methods: A case-control association study of 421 unrelated Chinese patients with high myopia and 401 control subjects matched in ethnicity and gender was undertaken. Genomic DNA was prepared from peripheral blood. All individuals were genotyped for 7 tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (tSNPs) across the IGF-1 gene region. Genotypic distribution was tested for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. The genotype and allele frequencies were evaluated using the χ(2) tests. Bonferroni corrections for multiple comparisons were performed.
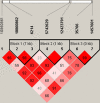
Results: The polymorphism of rs12423791 showed positive association with extreme myopia (p(allel)=0.006 and p(allel1 recessive model)=0.004, respectively) after Bonferroni correction for multiple testing and the haplotype GC of rs5742629-rs12423791 was also associated with extreme myopia (p=0.033) after 50,000 permutations for multiple comparisons.
Conclusions: The polymorphism of rs12423791 in IGF-1 may be associated with extreme myopia in the Chinese population and should be investigated further.
Figures
References
-
- Katz J, Tielsch JM, Sommer A. Prevalence and risk factors for refractive errors in an adult inner city population. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997;38:334–40. - PubMed
-
- Wong TY, Foster PJ, Hee J, Ng TP, Tielsch JM, Chew SJ, Johnson GJ, Seah SK. Prevalence and risk factors for refractive errors in adult Chinese in Singapore. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:2486–94. - PubMed
-
- Xinhua News Agency. Available from: http://news.xinhuanet.com/politics/2010-01/03/content_12745349.htm
-
- Paluru P, Ronan SM, Heon E, Devoto M, Wildenberg SC, Scavello G, Holleschau A, Mäkitie O, Cole WG, King RA, Young TL. New locus for autosomal dominant high myopia maps to the long arm of chromosome 17. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:1830–6. - PubMed
-
- Hosaka A. Population studies-myopia experience in Japan. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl. 1988;185:37–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
