Molecular pathways of notch signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 22509166
- PMCID: PMC3321637
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00081
Molecular pathways of notch signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
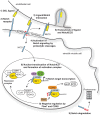
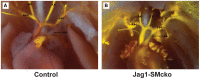
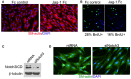
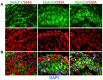
Notch signaling in the cardiovascular system is important during embryonic development, vascular repair of injury, and vascular pathology in humans. The vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) expresses multiple Notch receptors throughout its life cycle, and responds to Notch ligands as a regulatory mechanism of differentiation, recruitment to growing vessels, and maturation. The goal of this review is to provide an overview of the current understanding of the molecular basis for Notch regulation of VSMC phenotype. Further, we will explore Notch interaction with other signaling pathways important in VSMC.
Keywords: Notch; signaling; vascular smooth muscle.
Figures
References
-
- Arboleda-Velasquez J. F., Rampal R., Fung E., Darland D. C., Liu M., Martinez M. C., Donahue C. P., Navarro-Gonzalez M. F., Libby P., D’Amore P. A., Aikawa M., Haltiwanger R. S., Kosik K. S. (2005). CADASIL mutations impair Notch3 glycosylation by Fringe. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 1631–1639 10.1093/hmg/ddi171 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

