Multi-level interactions between the nuclear receptor TRα1 and the WNT effectors β-catenin/Tcf4 in the intestinal epithelium
- PMID: 22509275
- PMCID: PMC3317923
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034162
Multi-level interactions between the nuclear receptor TRα1 and the WNT effectors β-catenin/Tcf4 in the intestinal epithelium
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e93418
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Multi-Level Interactions between the Nuclear Receptor TRα1 and the WNT Effectors β-Catenin/Tcf4 in the Intestinal Epithelium.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 5;15(2):e0228994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228994. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32023305 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
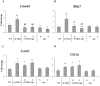
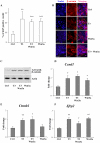
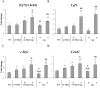
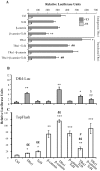
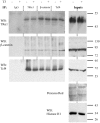
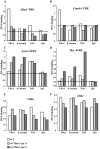
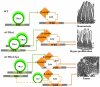
Intestinal homeostasis results from complex cross-regulation of signaling pathways; their alteration induces intestinal tumorigenesis. Previously, we found that the thyroid hormone nuclear receptor TRα1 activates and synergizes with the WNT pathway, inducing crypt cell proliferation and promoting tumorigenesis. Here, we investigated the mechanisms and implications of the cross-regulation between these two pathways in gut tumorigenesis in vivo and in vitro. We analyzed TRα1 and WNT target gene expression in healthy mucosae and tumors from mice overexpressing TRα1 in the intestinal epithelium in a WNT-activated genetic background (vil-TRα1/Apc mice). Interestingly, increased levels of β-catenin/Tcf4 complex in tumors from vil-TRα1/Apc mice blocked TRα1 transcriptional activity. This observation was confirmed in Caco2 cells, in which TRα1 functionality on a luciferase reporter-assay was reduced by the overexpression of β-catenin/Tcf4. Moreover, TRα1 physically interacted with β-catenin/Tcf4 in the nuclei of these cells. Using molecular approaches, we demonstrated that the binding of TRα1 to its DNA target sequences within the tumors was impaired, while it was newly recruited to WNT target genes. In conclusion, our observations strongly suggest that increased β-catenin/Tcf4 levels i) correlated with reduced TRα1 transcriptional activity on its target genes and, ii) were likely responsible for the shift of TRα1 binding on WNT targets. Together, these data suggest a novel mechanism for the tumor-promoting activity of the TRα1 nuclear receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cooperation between the thyroid hormone receptor TRalpha1 and the WNT pathway in the induction of intestinal tumorigenesis.Gastroenterology. 2010 May;138(5):1863-74. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.01.041. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20114049
-
The leukemia-associated Mllt10/Af10-Dot1l are Tcf4/β-catenin coactivators essential for intestinal homeostasis.PLoS Biol. 2010 Nov 16;8(11):e1000539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000539. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 21103407 Free PMC article.
-
The frizzled-related sFRP2 gene is a target of thyroid hormone receptor alpha1 and activates beta-catenin signaling in mouse intestine.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 9;284(2):1234-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806548200. Epub 2008 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19001373
-
Discovery of small molecule inhibitors of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting β-catenin/Tcf4 interactions.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jun;242(11):1185-1197. doi: 10.1177/1535370217708198. Epub 2017 May 5. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28474989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of TRα1 in cardiac repair: potential therapeutic implications.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:481482. doi: 10.1155/2014/481482. Epub 2014 Feb 9. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014. PMID: 24683435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thyroid hormones and their nuclear receptors: new players in intestinal epithelium stem cell biology?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Aug;71(15):2897-907. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1586-3. Epub 2014 Mar 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24604390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of SIRT1 in Cancer.Genes Cancer. 2013 Mar;4(3-4):97-104. doi: 10.1177/1947601912475079. Genes Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24020000 Free PMC article.
-
Teleost Metamorphosis: The Role of Thyroid Hormone.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jun 14;10:383. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00383. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31258515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid Hormone Receptor α Plays an Essential Role in Male Skeletal Muscle Myoblast Proliferation, Differentiation, and Response to Injury.Endocrinology. 2016 Jan;157(1):4-15. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1443. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 26451739 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt and lithium: a common destiny in the therapy of nervous system pathologies?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Apr;71(7):1123-48. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1378-1. Epub 2013 Jun 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 23749084 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, van de Wetering M, Begthel H, et al. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature. 2009;457:608–611. - PubMed
-
- Stappenbeck TS, Wong MH, Saam JR, Mysorekar IU, Gordon JI. Notes from some crypt watchers: regulation of renewal in the mouse intestinal epithelium. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10:702–709. - PubMed
-
- Sancho E, Batlle E, Clevers H. Signaling pathways in intestinal development and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:695–723. - PubMed
-
- Kress E, Samarut J, Plateroti M. Thyroid hormones and the control of cell proliferation or cell differentiation: paradox or duality? Mol Cell Endocrinol 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

