Unique cell type-specific junctional complexes in vascular endothelium of human and rat liver sinusoids
- PMID: 22509281
- PMCID: PMC3317944
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034206
Unique cell type-specific junctional complexes in vascular endothelium of human and rat liver sinusoids
Abstract
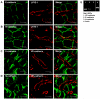
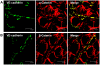
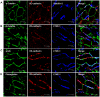
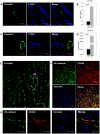
Liver sinusoidal endothelium is strategically positioned to control access of fluids, macromolecules and cells to the liver parenchyma and to serve clearance functions upstream of the hepatocytes. While clearance of macromolecular debris from the peripheral blood is performed by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) using a delicate endocytic receptor system featuring stabilin-1 and -2, the mannose receptor and CD32b, vascular permeability and cell trafficking are controlled by transcellular pores, i.e. the fenestrae, and by intercellular junctional complexes. In contrast to blood vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells in other organs, the junctional complexes of LSECs have not yet been consistently characterized in molecular terms. In a comprehensive analysis, we here show that LSECs express the typical proteins found in endothelial adherens junctions (AJ), i.e. VE-cadherin as well as α-, β-, p120-catenin and plakoglobin. Tight junction (TJ) transmembrane proteins typical of endothelial cells, i.e. claudin-5 and occludin, were not expressed by rat LSECs while heterogenous immunreactivity for claudin-5 was detected in human LSECs. In contrast, junctional molecules preferentially associating with TJ such as JAM-A, B and C and zonula occludens proteins ZO-1 and ZO-2 were readily detected in LSECs. Remarkably, among the JAMs JAM-C was considerably over-expressed in LSECs as compared to lung microvascular endothelial cells. In conclusion, we show here that LSECs form a special kind of mixed-type intercellular junctions characterized by co-occurrence of endothelial AJ proteins, and of ZO-1 and -2, and JAMs. The distinct molecular architecture of the intercellular junctional complexes of LSECs corroborates previous ultrastructural findings and provides the molecular basis for further analyses of the endothelial barrier function of liver sinusoids under pathologic conditions ranging from hepatic inflammation to formation of liver metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Perri R, Shah V. Chapter 5: Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells. In: Dufour JF, Clavien PA, editors. Signaling pathways in liver diseases. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2005. pp. 53–62.
-
- Si-Tayeb K, Lemaigre FP, Duncan SA. Organogenesis and development of the liver. Dev Cell. 2010;18:175–189. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ Res. 2007;100:174–190. - PubMed
-
- Steinhoff G, Behrend M, Schrader B, Duijvestijn AM, Wonigeit K. Expression patterns of leukocyte adhesion ligand molecules on human liver endothelia. Lack of ELAM-1 and CD62 inducibility on sinusoidal endothelia and distinct distribution of VCAM-1, ICAM-1, ICAM-2, and LFA-3. Am J Pathol. 1993;142:481–488. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

