Epigenetic factors in cancer risk: effect of chemical carcinogens on global DNA methylation pattern in human TK6 cells
- PMID: 22509344
- PMCID: PMC3324488
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034674
Epigenetic factors in cancer risk: effect of chemical carcinogens on global DNA methylation pattern in human TK6 cells
Abstract
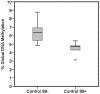
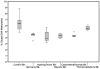
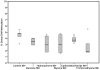
In the current study, we assessed the global DNA methylation changes in human lymphoblastoid (TK6) cells in vitro in response to 5 direct and 10 indirect-acting genotoxic agents. TK6 cells were exposed to the selected agents for 24 h in the presence and/or absence of S9 metabolic mix. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was used for quantitative profiling of 5-methyl-2'-deoxycytidine. The effect of exposure on 5-methyl-2'-deoxycytidine between control and exposed cultures was assessed by applying the marginal model with correlated residuals on % global DNA methylation data. We reported the induction of global DNA hypomethylation in TK6 cells in response to S9 metabolic mix, under the current experimental settings. Benzene, hydroquinone, styrene, carbon tetrachloride and trichloroethylene induced global DNA hypomethylation in TK6 cells. Furthermore, we showed that dose did not have an effect on global DNA methylation in TK6 cells. In conclusion we report changes in global DNA methylation as an early event in response to agents traditionally considered as genotoxic.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of chemical mutagens and carcinogens on gene expression profiles in human TK6 cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39205. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039205. Epub 2012 Jun 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22723965 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of benzene and its metabolites on global DNA methylation in human normal hepatic L02 cells.Environ Toxicol. 2014 Jan;29(1):108-16. doi: 10.1002/tox.20777. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Environ Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 21953684
-
Reduced hepatic global hydroxymethylation in mice treated with non-genotoxic carcinogens is transiently reversible with a methyl supplemented diet.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 15;415:115439. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115439. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33549593
-
A Tox21 Approach to Altered Epigenetic Landscapes: Assessing Epigenetic Toxicity Pathways Leading to Altered Gene Expression and Oncogenic Transformation In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 1;18(6):1179. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061179. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28587163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylome alterations in chemical carcinogenesis.Cancer Lett. 2013 Jun 28;334(1):39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.09.010. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23010082 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the metabolic activation of environmental carcinogens in mouse embryonic stem cells and mouse embryonic fibroblasts.Toxicol In Vitro. 2015 Feb;29(1):34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2014.09.004. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015. PMID: 25230394 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic alterations induced by genotoxic occupational and environmental human chemical carcinogens: A systematic literature review.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2016 Apr-Jun;768:27-45. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2016. PMID: 27234561 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased mitochondrial DNA content in association with exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in house dust during wintertime: from a population enquiry to cell culture.PLoS One. 2013 May 3;8(5):e63208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063208. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658810 Free PMC article.
-
Placental DNA hypomethylation in association with particulate air pollution in early life.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2013 Jun 7;10:22. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-10-22. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23742113 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative cancer risk assessment and local mortality burden for ambient air pollution in an eastern Mediterranean City.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Jun;24(16):14151-14162. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9000-y. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28417329
References
-
- Ziech D, Franco R, Pappa A, Malamou-Mitsi V, Georgakila S, et al. The role of epigenetics in environmental and occupational carcinogenesis. Chemico-Biological Interactions. 2010;188:340–349. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 2004;10:789–799. - PubMed
-
- Hussain SP, Schwank J, Staib F, Wang XW, Harris CC. TP53 mutations and hepatocellular carcinoma: insights into the etiology and pathogenesis of liver cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:2166–2176. - PubMed
-
- Rundle A. Carcinogen-DNA adducts as a biomarker for cancer risk. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis. 2006;600:23–36. - PubMed
-
- Poirier MC. Chemical-induced DNA damage and human cancer risk. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:630–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

