Mixed adjuvant formulations reveal a new combination that elicit antibody response comparable to Freund's adjuvants
- PMID: 22509385
- PMCID: PMC3324409
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035083
Mixed adjuvant formulations reveal a new combination that elicit antibody response comparable to Freund's adjuvants
Abstract
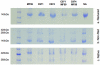
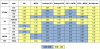
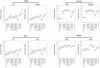
Adjuvant formulations capable of inducing high titer and high affinity antibody responses would provide a major advance in the development of vaccines to viral infections such as HIV-1. Although oil-in-water emulsions, such as Freund's adjuvant (FCA/FIA), are known to be potent, their toxicity and reactogenicity make them unacceptable for human use. Here, we explored different adjuvants and compared their ability to elicit antibody responses to FCA/FIA. Recombinant soluble trimeric HIV-1 gp140 antigen was formulated in different adjuvants, including FCA/FIA, Carbopol-971P, Carbopol-974P and the licensed adjuvant MF59, or combinations of MF59 and Carbopol. The antigen-adjuvant formulation was administered in a prime-boost regimen into rabbits, and elicitation of antigen binding and neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) was evaluated. When used individually, only FCA/FIA elicited significantly higher titer of nAbs than the control group (gp140 in PBS (p<0.05)). Sequential prime-boost immunizations with different adjuvants did not offer improvements over the use of FCA/FIA or MF59. Remarkably however, the concurrent use of the combination of Carbopol-971P and MF59 induced potent adjuvant activity with significantly higher titer nAbs than FCA/FIA (p<0.05). This combination was not associated with any obvious local or systemic adverse effects. Antibody competition indicated that the majority of the neutralizing activities were directed to the CD4 binding site (CD4bs). Increased antibody titers to the gp41 membrane proximal external region (MPER) and gp120 V3 were detected when the more potent adjuvants were used. These data reveal that the combination of Carbopol-971P and MF59 is unusually potent for eliciting nAbs to a variety of HIV-1 nAb epitopes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Binley JM, Arshad H, Fouts TR, Moore JP. An investigation of the high-avidity antibody response to glycoprotein 120 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1997;13:1007–1015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

